Explore AI-driven customer engagement in banking with real use cases, voice AI, compliance requirements, and how banks scale real-time engagement. Read more.

Kaushal Choudhary
Updated on
February 3, 2026 at 4:01 PM

A customer calls their bank because a payment failed. They expect the system to know who they are, why the payment failed, and what needs to happen next. Instead, they repeat details, wait on hold, and receive a generic explanation that arrives too late to be useful.
Moments like this explain why banks started rethinking engagement itself. AI-driven customer engagement in banking emerged from this gap, not as a chatbot trend, but as a response to real breakdowns in speed, context, and execution across everyday financial interactions.
This shift accelerated as banks began embedding AI directly into servicing, voice interactions, onboarding, and fraud response. The momentum is reflected in market growth. The AI in Banking market is projected to reach USD 90.97 billion by 2030, driven by institutions moving away from static journeys toward real-time, intent-led engagement. As expectations reset, AI-driven customer engagement in banking has become a core operating capability rather than an experimental layer.
In this guide, we examine how this evolution took shape, where AI is already delivering measurable impact, and what the next phase of customer engagement looks like for banks building at scale.
Key Takeaways
Engagement Has Shifted to Real Time: AI-driven customer engagement in banking acts on live transactions, voice interactions, and behavioral signals rather than scheduled journeys.
Voice Remains the Critical Channel: Payment issues, fraud, and identity verification still happen on calls, making low-latency voice AI central to engagement.
Execution Quality Determines Impact: Sub-second inference, explainable decisions, and governed escalation separate production systems from pilots.
Value Comes from Embedded Workflows: The strongest results appear where AI operates directly inside servicing, risk, and decisioning workflows.
Scale Requires Infrastructure Thinking: Banks succeed when AI is treated as operational infrastructure, not an experimental layer.
What AI-Driven Customer Engagement Means for Banks
AI-driven customer engagement in banking describes how banks use artificial intelligence to decide when, how, and why a customer interaction should occur, based on real signals rather than predefined journeys.
At its core, it is characterised by:
Decisions driven by transaction events, account activity, and interaction history.
Engagement triggered by specific customer actions rather than scheduled campaigns.
Responses are generated dynamically instead of pulled from fixed templates.
In this model, AI-driven customer engagement in banking operates continuously.
Banks use it to:
Detect moments such as balance changes, payment failures, or unusual activity.
Initiate communication at the point where an action is required.
Adjust tone, channel, and content based on the situation, not customer category.
Functionally, AI-driven customer engagement in banking sits between data systems and customer-facing channels.
It connects:
Core banking and payment systems.
Digital touchpoints such as mobile apps, web portals, and contact centres.
Interaction outcomes from previous service or support conversations.
This structure allows banks to act during live financial moments, while keeping engagement logic traceable, repeatable, and suitable for regulated environments.
Explore which platforms meet latency, compliance, and scale demands in Top AI voice agents for BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance)
Core Capabilities Powering AI-Driven Customer Engagement
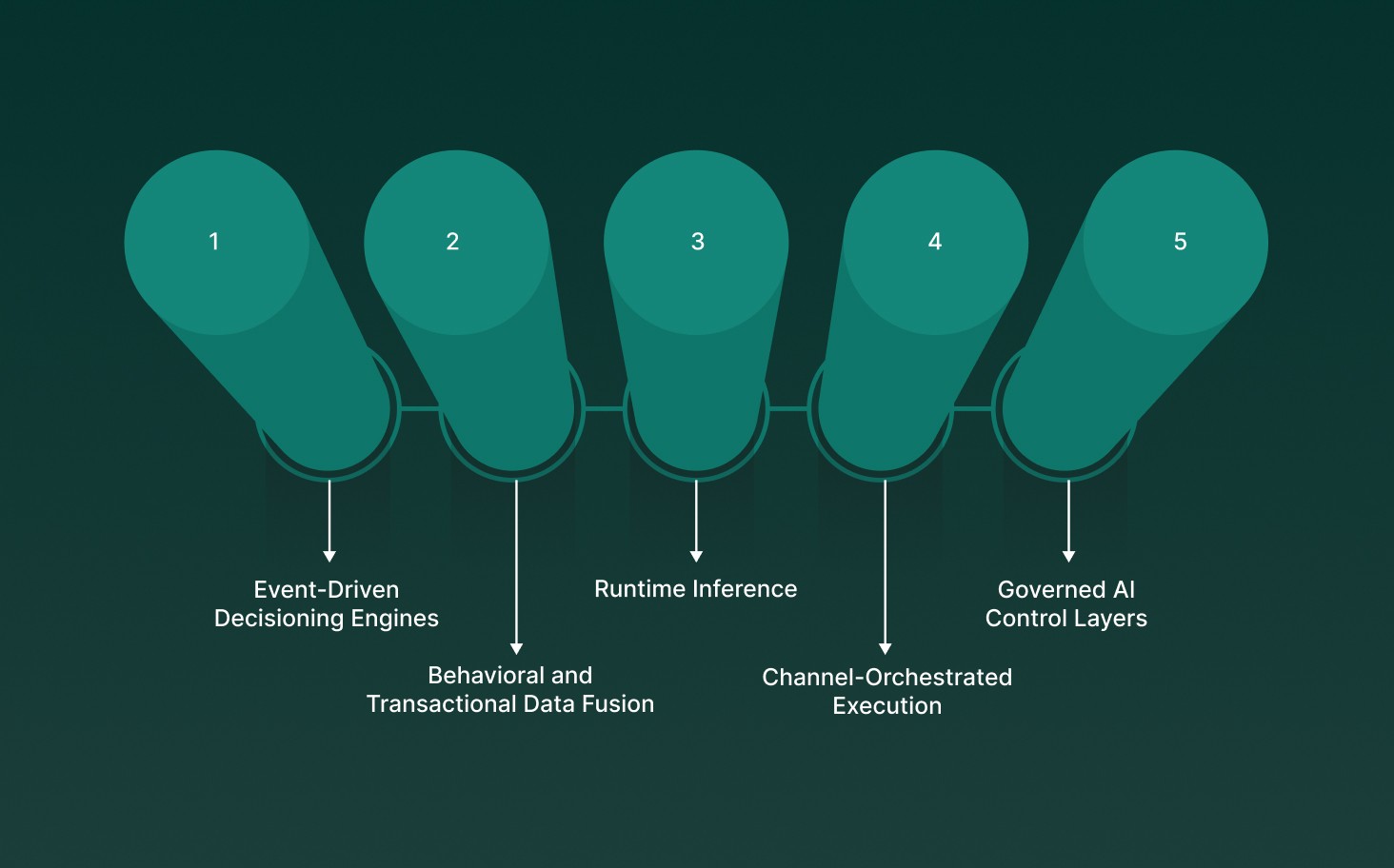
AI-driven customer engagement in banking is allowed by a set of tightly coupled technical capabilities that allow banks to sense, decide, and act during live customer interactions. These capabilities operate across data, models, and execution layers, turning customer signals into precise engagement actions under strict performance and compliance constraints.
Event-Driven Decisioning Engines: Real-time processors ingest signals such as transaction failures, balance thresholds, fraud flags, or session activity and trigger engagement logic within milliseconds, replacing batch-based campaign execution.
Behavioral and Transactional Data Fusion: AI systems correlate core banking data, digital interaction logs, and historical service outcomes to form a unified, time-ordered context for each customer interaction.
Runtime Inference and Intent Resolution: Models perform inference at interaction time to classify intent, urgency, and next action, allowing banks to respond during live sessions rather than after customer drop-off.
Channel-Orchestrated Execution: Engagement logic dynamically selects voice, chat, push, or human escalation based on latency requirements, interaction complexity, and regulatory constraints tied to the use case.
Governed AI Control Layers: Model outputs are constrained by policy rules, audit logs, and access controls, guaranteeing explainability, traceability, and compliance across regulated banking workflows.
Together, these capabilities allow banks to move from static engagement workflows to real-time, system-driven execution while maintaining operational control and regulatory accountability.
High-Impact AI-Driven Customer Engagement Use Cases in Banking
AI-driven customer engagement in banking delivers its strongest impact where AI systems operate directly within live customer interactions, transactional workflows, and regulated decision paths. These use cases represent production-grade deployments where engagement logic is embedded into core banking, contact center, risk, and data platforms.
1. Conversational AI and Real-Time Voice Banking
Conversational AI systems powered by large language models and retrieval-augmented generation operate as real-time engagement layers across voice, chat, mobile, and web channels.
Stateful Multi-Channel Context Management: Conversations persist across channels with maintained authentication, intent, and session history.
Live Core-System Retrieval: RAG layers query account data, transaction history, eligibility rules, and compliance status during interaction runtime.
Confidence-Scored Escalation: AI confidence thresholds trigger human handoff with full conversation state and risk context attached.
Example: Bank of America’s Erica handled 676 million customer interactions in 2024 by maintaining conversational context across digital and voice channels.
2. AI-Powered Loan Application Processing and Automated Decisioning
AI-driven underwriting systems execute loan origination workflows end to end, compressing decision timelines without degrading credit quality.
Intelligent Document Processing Pipelines: OCR and extraction models classify and validate payslips, bank statements, tax returns, and identity documents.
Parallel Credit and Risk Scoring: Behavioral, income consistency, and credit risk models execute simultaneously for instant preliminary decisions.
Explainable Decision Artifacts: Each approval or rejection generates an auditable rationale tied to data inputs and thresholds.
Example: Solvexia banks' reconciliations deliver clear, auditable workflows for each reconciliation while reducing errors by 98%.
3. Real-Time Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI-driven fraud systems analyze transactions at millisecond latency across digital, voice, and card channels.
High-Dimensional Transaction Analysis: Systems evaluate a lot of transaction attributes, including velocity, merchant behavior, and geolocation.
Behavioral and Voice Biometrics Fusion: Keystroke dynamics, device fingerprints, and voice signals detect impersonation and deepfake attacks.
Cross-Entity Pattern Recognition: Unsupervised models identify coordinated fraud and money laundering across multiple accounts.
Example: Stripe Radar evaluates more than 1,000 transaction-level signals and computes fraud likelihood in under 100 milliseconds, allowing decisions to be made before payment authorization completes.
4. Predictive Customer Churn and Proactive Retention
Machine learning models identify disengagement risk well before accounts become dormant.
Time-Series Behavioral Modeling: Login cadence, balance movement, transaction diversity, and service interactions feed churn models.
Interpretable Risk Attribution: Models surface the top drivers of churn per customer rather than opaque risk scores.
Prescriptive Retention Actions: Systems recommend fee waivers, product changes, or relationship manager outreach.
Example: An AI company worked with bank domain experts to retrospectively identify more than 20,000 instances of permanent balance attrition across a 31-month historical dataset, establishing labeled ground truth for churn pattern analysis.
5. Dynamic Personalization and Real-Time Recommendation Engines
Decision engines generate next-best actions during live customer sessions.
Streaming Feature Engineering: Contextual features are computed from real-time transaction events rather than batch summaries.
Hybrid Recommendation Models: Collaborative and content-based filtering adapt to evolving customer needs.
Continuous Experimentation: Built-in A/B testing optimizes recommendations against conversion and lifetime value metrics.
Example: JPMorgan Chase stated that it is targeting up to $1.5 billion in enterprise value from artificial intelligence initiatives, driven by firm-wide investments in data, infrastructure, and AI-enabled efficiencies across banking operations and customer-facing platforms.
6. Voice Biometric Authentication and Frictionless Identity Verification
Voice biometrics replace passwords and PINs for secure, low-friction customer authentication.
Polyglot Voiceprint Modeling: Neural networks normalize accents and dialects across multilingual populations.
Continuous Session Authentication: Identity is verified throughout the interaction to detect mid-call impersonation.
Risk-Adaptive Authorization: Voice biometrics combine with transaction risk signals to scale authentication strength.
Example: Large retail banks use voice biometric authentication at scale to secure call-center interactions, enabling identity verification for tens of millions of customers without relying on PINs or security questions.
These use cases define where AI-driven customer engagement in banking functions as a core operational infrastructure. The most effective deployments integrate conversational AI, predictive modeling, real-time decisioning, and compliance controls into unified systems that operate under strict latency, scale, and regulatory constraints.
Run real-time, policy-controlled voice conversations at scale with Smallest.ai, built for sub-second latency, deterministic behavior, and compliance-safe execution in live debt collection workflows.
Operational and Compliance Considerations for AI in Banking

AI-driven customer engagement in banking operates inside regulated environments where system behavior, data access, and decision outcomes must remain controlled, explainable, and auditable. Operational and compliance considerations determine whether AI systems can be deployed beyond pilots and safely embedded into core banking workflows.
Model Explainability and Decision Traceability: AI systems must generate machine-readable explanations that link outputs to specific data inputs, thresholds, and rules, enabling post-hoc review by risk teams and regulators.
Data Access Control and Segmentation: Fine-grained permissioning governs which models can access PII, financial data, and behavioral signals, enforced through role-based access and environment isolation.
Latency and Reliability Guarantees: AI components integrated into transaction flows or live conversations must meet deterministic latency SLAs to avoid service degradation or failed authorizations.
Human-in-the-Loop Enforcement: Clear escalation thresholds define when automated decisions pause and route to human review, particularly for credit, fraud, and customer-impacting actions.
Audit Logging and Regulatory Retention: Every AI-driven interaction is logged with timestamps, model versions, data sources, and actions taken to satisfy retention, audit, and supervisory review requirements.
Together, these considerations define whether AI systems can operate as production-grade infrastructure in banking while maintaining regulatory confidence and operational stability.
Common Challenges Banks Face During Adoption
AI-driven customer engagement in banking often stalls not because of model capability but because of constraints in data architecture, operational readiness, and regulatory execution. These challenges emerge when banks move from controlled pilots to systems that must operate continuously across transactions, channels, and jurisdictions.
Challenge Area | Where It Breaks in Practice | Why It Matters |
Legacy Core System Coupling | AI systems cannot subscribe to real-time events from batch-oriented core banking platforms. | Engagement decisions miss live financial moments and revert to delayed outreach. |
Fragmented Data Lineage | Transaction, interaction, and identity data lack a unified source of truth. | Models operate on partial context, increasing error rates and regulatory risk. |
Production Latency Constraints | Inference pipelines exceed acceptable response times for live calls or payments. | Customer experience degrades, or automated actions are bypassed. |
Model Governance at Scale | Versioning, retraining, and rollback processes are not operationalized. | Banks struggle to explain which model produced which decision during audits. |
Channel Execution Gaps | AI decisions are made, but cannot be executed consistently across voice, chat, and digital channels. | Engagement logic fragments, creating inconsistent customer outcomes. |
Human Escalation Design | Clear thresholds for AI-to-human handoff are not defined. | Agents receive low-quality escalations or miss high-risk cases. |
Regulatory Change Management | Policy updates are not reflected promptly in AI logic. | Systems continue to act on outdated compliance rules. |
These challenges highlight that successful adoption depends less on model sophistication and more on execution discipline across infrastructure, governance, and operational design.
See how automation and AI converge to drive execution inside core banking workflows in Top 16+ RPA Use Cases Transforming the Banking Industry
What the Next Phase of AI-Driven Customer Engagement Looks Like
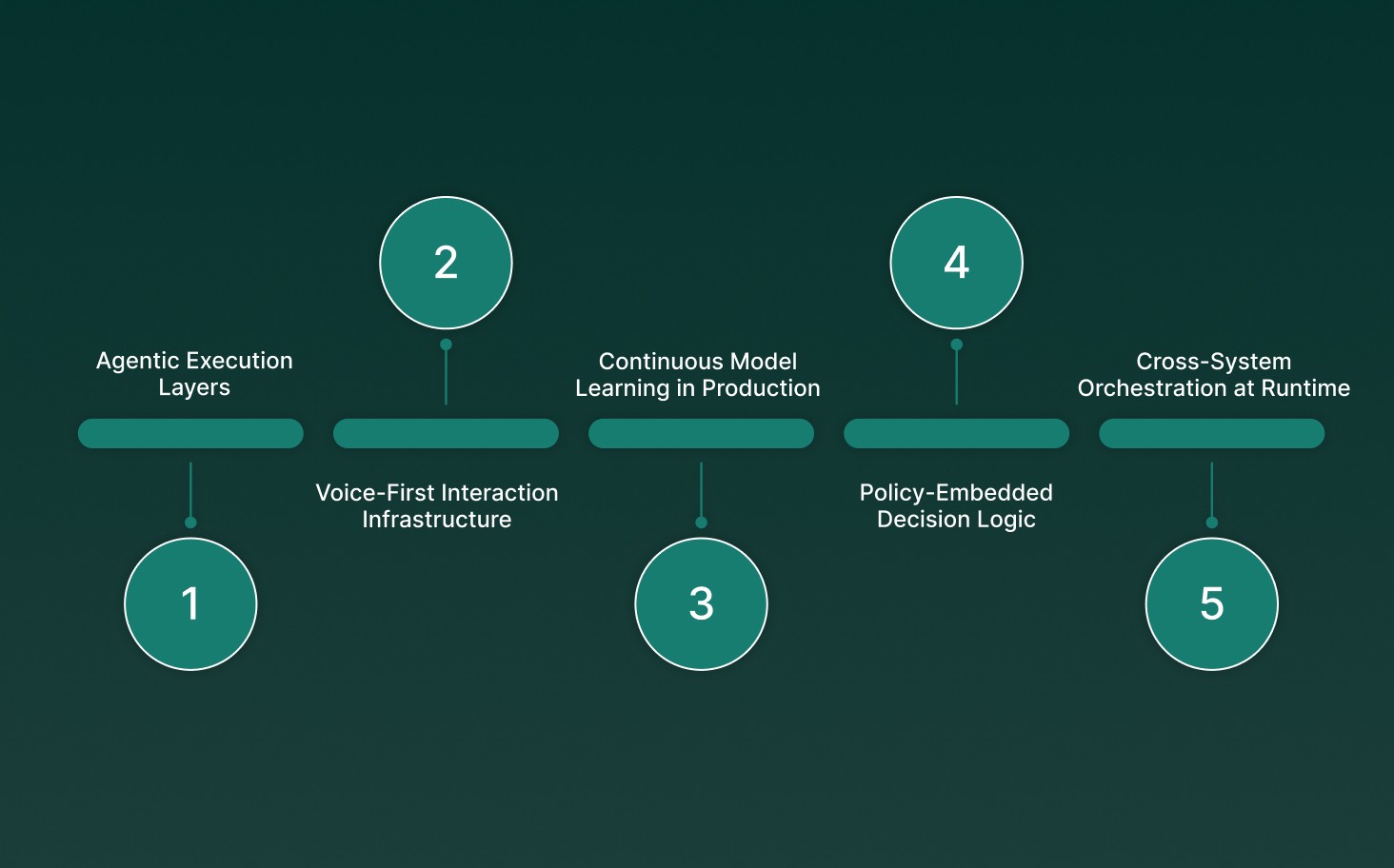
The next phase of AI-driven customer engagement in banking is defined by systems that act autonomously within strict controls, operate in real time across voice and digital channels, and integrate directly with core banking execution layers. This phase shifts AI from assistive tooling to always-on infrastructure.
Agentic Execution Layers: AI agents coordinate multi-step actions such as verification, resolution, and follow-up without hardcoded workflows, while remaining constrained by policy and permission boundaries.
Voice-First Interaction Infrastructure: Real-time voice AI operates as a primary engagement surface, handling complex conversations with low latency and full context persistence across sessions.
Continuous Model Learning in Production: Models retrain using post-interaction outcomes, error cases, and edge conditions without disrupting live systems or violating governance rules.
Policy-Embedded Decision Logic: Regulatory and risk policies are encoded directly into decision engines, allowing automatic enforcement as conditions change.
Cross-System Orchestration at Runtime: Engagement decisions trigger coordinated actions across core banking, CRM, fraud, and contact center platforms in a single execution flow.
This next phase positions AI-driven customer engagement in banking as core operational infrastructure, governing how banks listen, decide, and act at scale.
Smallest.ai and Real-Time Voice Execution for Banking
Smallest.ai addresses the most failure-prone layer of AI-driven customer engagement in banking: live voice interactions where latency, accuracy, and control determine outcomes. The platform is designed for production banking environments where conversations must execute actions, not generate responses.
Sub-Second Voice Latency: Real-time speech-to-intent and response generation operates within strict latency bounds required for payment issues, authentication, and fraud-sensitive conversations.
Stateful Call Context Handling: Conversations maintain session memory across multi-turn voice interactions, preserving intent, authentication state, and prior actions without restarts.
Action-Oriented Voice Agents: Voice agents trigger downstream banking actions such as ticket creation, escalations, or workflow execution rather than stopping at informational responses.
Bank-Grade Deployment Control: Supports on-premise and controlled cloud environments with full ownership over data paths, inference behavior, and audit logging.
Voice-Native Compliance Hooks: Call flows integrate consent capture, disclosure enforcement, and interaction recording aligned to banking regulatory requirements.
Smallest.ai allows banks to run voice as an execution surface, not a support channel. For teams evaluating how to handle high-volume, high-risk conversations in real time, this is where conversational AI becomes operational.
Final Thoughts!
AI-driven customer engagement in banking has reached a point where differentiation comes from execution quality rather than intent. Banks that succeed treat engagement as a real-time system problem, not a messaging problem.
The gap is no longer between AI and non-AI banks, but between institutions that can act in real-time and those that respond after the fact. This shift places pressure on latency, reliability, voice handling, and orchestration across channels, areas where architectural choices matter more than feature checklists.
This is where platforms built for real-time voice and conversational execution become critical. Smallest.ai focuses on the hardest layer of engagement, running low-latency, production-grade voice
AI that operates inside live banking interactions rather than around them. If you are evaluating how to support high-volume calls, sensitive conversations, or real-time decision-making without compromising control, it is worth seeing how this works in practice.
Talk to a voice expert and see how Smallest.ai powers real-time banking conversations at scale.
Answer to all your questions
Have more questions? Contact our sales team to get the answer you’re looking for

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now