Explore 6 proven bank bot use cases banks deploy today, covering fraud response, card controls, payments, collections, and real-time voice support at scale.

Ranjith M S
Updated on
February 4, 2026 at 10:06 AM

A customer calls their bank to check a failed transaction. They wait, repeat details, and move between menus before reaching an agent. For banking teams, this moment is familiar and costly. For customers, it feels avoidable. That gap between expectation and reality is exactly why interest in a bank bot has grown across service, operations, and collections teams.
When teams search for a bank bot, they are usually not looking for experimentation. They want faster resolution for routine requests, fewer inbound calls during peak hours, and tighter control over regulated conversations. The focus is practical support at scale without adding pressure on agents or compliance teams.
This shift is reflected in market growth. By 2033, the banking chatbot market is forecasted to reach USD 14.12 billion, driven by real-world deployments across voice and chat channels.
In this guide, we break down how bank bots are used today, where banking AI chatbots fit, and how platforms such as conversational voice agents, IVR automation tools, and AI-powered banking assistants are shaping modern banking operations.
Key Takeaways
Rule-Bound Automation Wins: Bank bots succeed where workflows are fixed, audited, and tied directly to core banking systems rather than open-ended conversations.
Speed Is A Risk Control: Immediate actions like card blocking and fraud intake reduce exposure by executing safeguards within the same interaction.
Voice Handles Pressure Better: Voice bank bots absorb peak-hour call spikes and time-sensitive issues that chat interfaces struggle to resolve quickly.
Collections See Measurable Lift: Early-stage reminder calls and payment intent capture reduce manual follow-ups and agent workload in collections teams.
Production Bots Need Infrastructure: Sub-100 ms latency, concurrent call handling, and on-prem deployment separate real deployments from pilots.
Why Banks Are Adopting Bank Bots at Scale
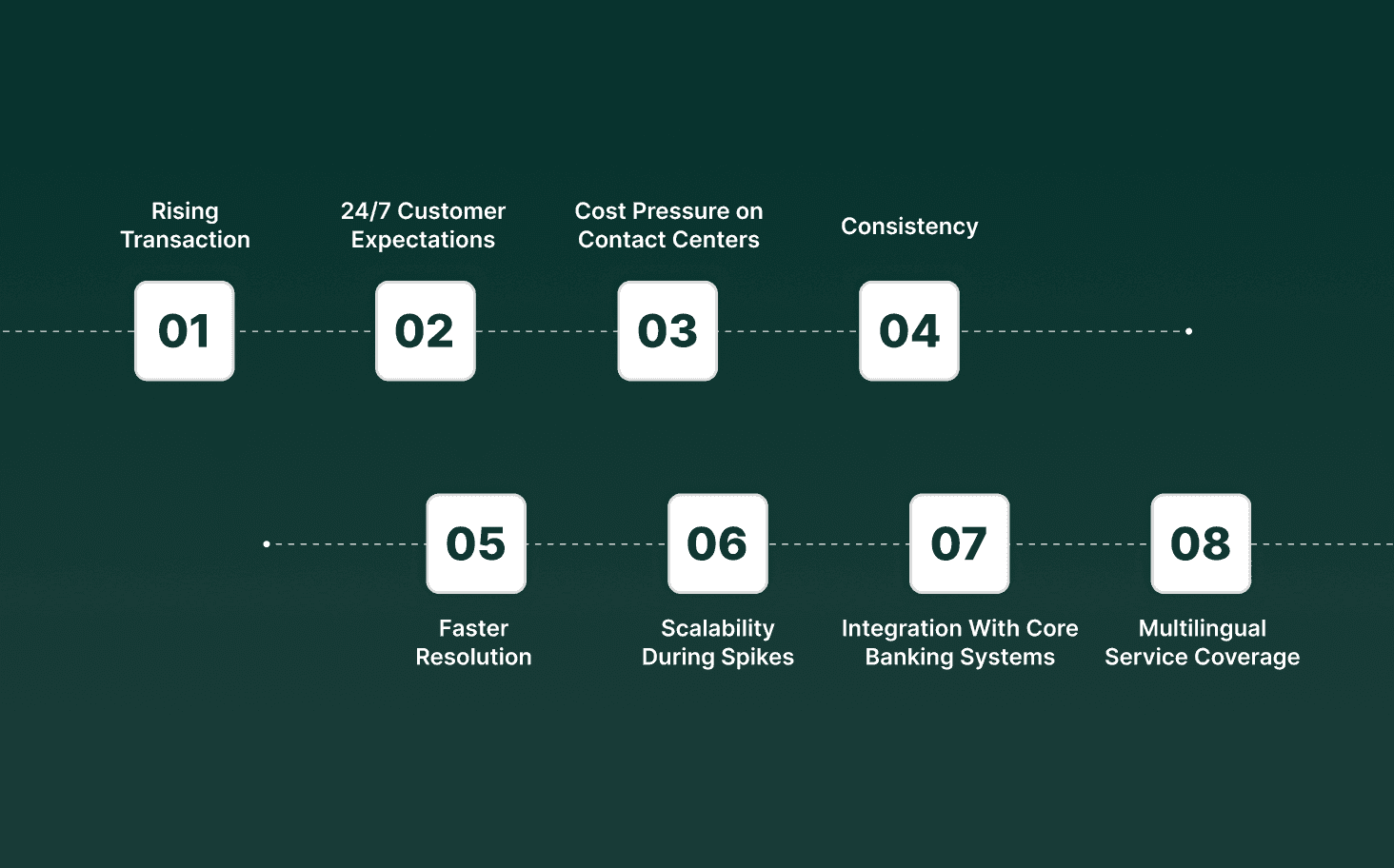
Banks are adopting bank bots to handle high-volume, rules-driven customer interactions where speed, accuracy, and consistency matter. Adoption is driven by operational pressure, regulatory expectations, and rising customer demand for instant service across channels.
Rising Transaction and Query Volumes: Bank bots handle balance checks, transaction status, card issues, and account queries that make up a large share of daily inbound traffic.
24/7 Customer Expectations: Customers expect support outside branch hours, including nights and weekends, without delays or callbacks.
Cost Pressure on Contact Centers: Repetitive queries consume agent time, increasing staffing costs without adding customer value.
Consistency in Regulated Responses: Bank bots deliver approved, policy-aligned responses every time, reducing the risk of compliance drift.
Faster Resolution for Simple Requests: Routine tasks get resolved in seconds, cutting queue lengths for live agents.
Scalability During Spikes: Bots handle sudden surges during outages, payment failures, or regulatory announcements without service degradation.
Integration With Core Banking Systems: Modern bank bots connect directly to account systems, CRMs, and payment platforms for real-time responses.
Multilingual Service Coverage: Bots support multiple languages without hiring region-specific agent teams.
Banks adopt bank bots at scale because they absorb predictable workload, protect service quality under pressure, and allow human agents to focus on complex, high-risk, or high-value interactions.
See how teams expand support capacity, reduce wait times, and maintain consistent service as volumes grow. Scaling Customer Support with AI Chatbot Solutions
Top Use Cases of Bank Bots in Modern Banking
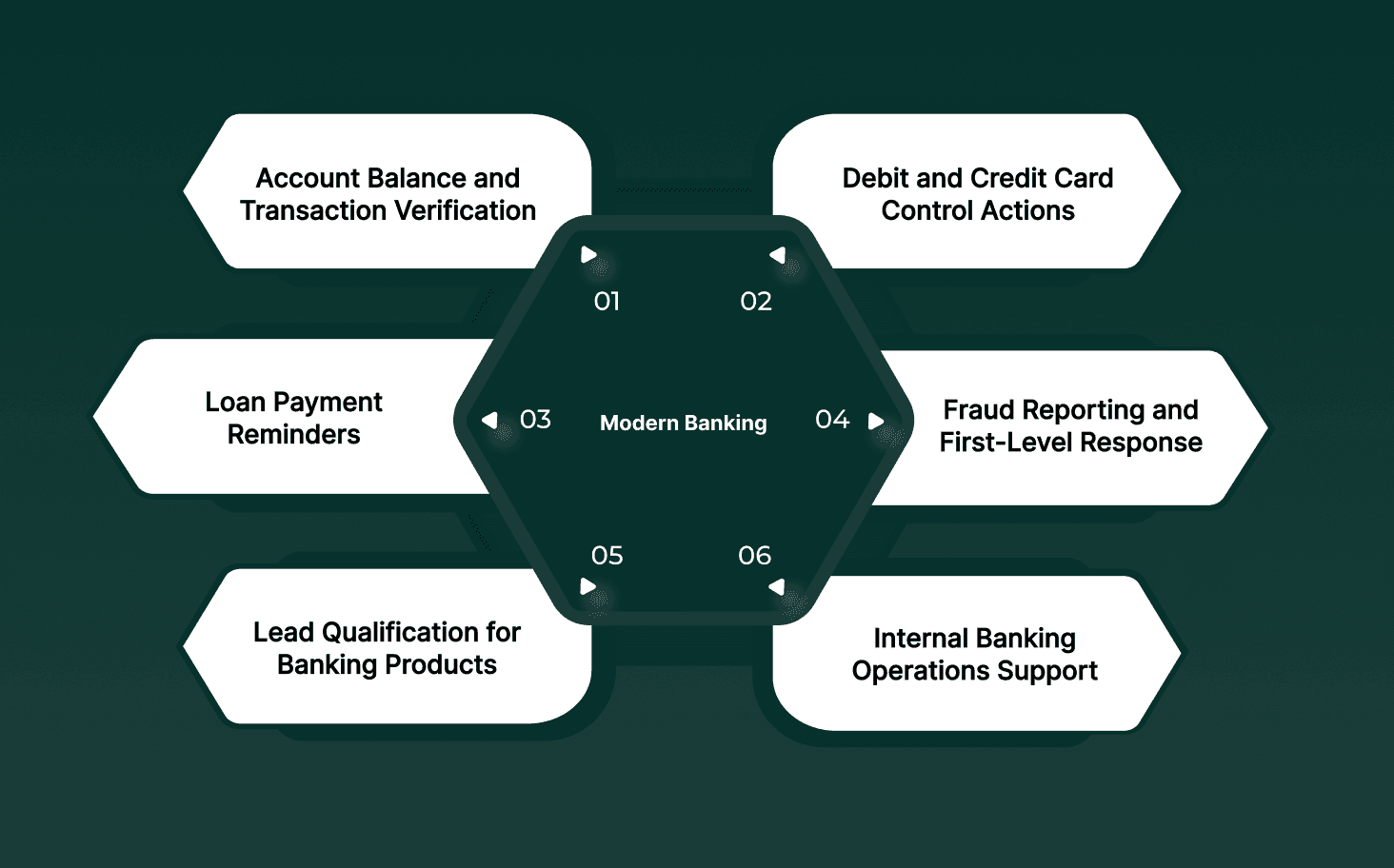
Bank bots are deployed where actions are predictable, data access is controlled, and outcomes can be verified against core banking systems. These use cases reflect production deployments, not experimental pilots.
1. Account Balance and Transaction Verification
Bank bots resolve the highest-volume inbound queries tied directly to core account systems.
Real-Time Balance Retrieval: Pulls ledger and available balances directly from the core banking system.
Last-N Transaction Lookups: Reads recent debit and credit entries with timestamps and reference IDs.
Transaction Failure Explanations: Maps failure codes from payment rails to customer-readable reasons.
Example: A customer calls to verify whether a card debit posted successfully. The bot reads the transaction status and reference number from the core system without agent involvement.
2. Debit and Credit Card Control Actions
Bots handle card actions where speed directly reduces fraud exposure.
Immediate Card Blocking: Executes block commands after OTP or IVR authentication.
Temporary Card Unblocks: Restores access within predefined time windows.
Card Replacement Tracking: Reports issuance and dispatch status from card management systems.
Example: After noticing suspicious activity, a customer blocks their card through a voice bot within the same call, without waiting for an agent.
3. EMI, Credit Card, and Loan Payment Reminders
Bots automate early-stage collections using fixed scripts and escalation rules.
Scheduled Reminder Calls: Triggers outbound reminders based on due-date logic.
Payment Intent Capture: Records promised payment dates in the collections system.
Non-Response Escalation: Flags accounts for agent follow-up after defined retries.
Example: A bot contacts customers three days before EMI due dates and logs payment intent, reducing manual outbound call volume.
4. Fraud Reporting and First-Level Response
Bots serve as the first intake layer for suspected fraud cases.
Structured Incident Capture: Records transaction IDs, dates, and channels involved.
Immediate Risk Actions: Triggers card or account restrictions where policy allows.
Case Creation for Analysts: Pushes call data and metadata into fraud case systems.
Example: A customer reports an unauthorized transaction, and the bot blocks the card and opens a fraud case with full call context attached.
5. Lead Qualification for Banking Products
Bots filter inbound sales interest before human follow-up.
Product Interest Confirmation: Verifies intent for loans, cards, or deposits.
Eligibility Data Collection: Captures income range, location, and employment type.
Routing to Relationship Managers: Assigns qualified leads based on branch or segment rules.
Example: A chatbot qualifies a personal loan inquiry and schedules a callback with the assigned relationship manager.
6. Internal Banking Operations Support
Banks deploy bots internally to reduce operational friction for staff.
SOP and Policy Retrieval: Answers employee queries using approved internal documents.
System Workflow Guidance: Provides step-by-step instructions for CRM and core actions.
Ticket Reduction: Deflects repetitive IT and HR queries from support desks.
Example: A branch employee asks how to reverse a failed transaction, and the bot returns the exact system steps based on internal SOPs.
Modern bank bot use cases are tightly scoped, system-connected, and governed by rules. Banks deploy them where accuracy, speed, and auditability matter, not as open-ended conversational tools.
Common Misconceptions Around Bank Bots in Banking
Bank bots are often misunderstood due to early chatbot limitations and overhyped claims. In practice, modern bank bots are deployed with strict controls, narrow scopes, and clear handoff rules to meet banking requirements.
Bank Bots Replace Human Agents: Bank bots handle repeatable, low-risk tasks, while complex issues, disputes, and exceptions still route to trained agents.
Bots Can Access Any Customer Data: Bank bots only access data permitted by role-based controls, audit policies, and predefined workflows.
All Banking Conversations Are Automated: Sensitive actions such as dispute resolution, loan restructuring, or fraud claims often require human verification.
Bots Make Independent Financial Decisions: Bank bots follow scripted logic and system rules; they do not approve credit, change limits, or waive fees autonomously.
Bots Increase Compliance Risk: Properly deployed bots reduce variance by delivering approved responses and logging every interaction for audits.
Bots Work Without Ongoing Oversight: Bank bots require continuous monitoring, policy updates, and model review to stay accurate and compliant.
One Bot Fits Every Banking Function: Banks deploy separate bots for service, collections, onboarding, and internal support due to different data access and risk profiles.
Bots Eliminate Customer Friction Entirely: Bots improve speed and consistency but still rely on clean data, clear prompts, and timely human fallback.
Most misconceptions stem from assuming bank bots operate without boundaries. In reality, banks deploy them within defined scopes, controls, and escalation paths designed to support compliance and operational stability.
Compare how leading platforms handle live conversations, system access, and scale across real customer environments. Top 11 Conversational AI Platforms In 2025
Voice Bank Bots vs Traditional Banking Chatbots
Voice bank bots and traditional banking chatbots serve different interaction needs. The difference lies in channel behavior, task suitability, and risk handling rather than capability depth.
Aspect | Voice Bank Bots | Traditional Banking Chatbots |
Primary Channel | Phone calls and IVR replacements | Web, mobile apps, and messaging platforms |
User Intent Type | Urgent, transactional, time-sensitive requests | Informational and self-serve actions |
Input Handling | Spoken language with real-time intent detection | Typed input with structured flows |
Authentication Methods | Caller ID, OTPs, voice prompts, and IVR-style checks | App login, OTPs, and in-session verification |
Error Tolerance | Lower tolerance for misinterpretation due to call cost | Higher tolerance due to visible correction |
Average Interaction Length | Short, focused exchanges | Longer, multi-step conversations |
Accessibility | Suitable for users without smartphones or strong literacy | Requires reading and typing ability |
Escalation Path | Live agent takeover during the same call | Ticket creation or chat transfer |
Operational Cost Impact | Reduces agent call load during peak hours | Reduces chat and email volume |
Voice bank bots address real-time, high-pressure service needs on calls, while traditional banking chatbots handle structured digital interactions. Banks deploy both to cover distinct customer behaviors rather than choosing one over the other.
Deploy real-time voice agents with low latency, live system access, and enterprise-grade control using smallest.ai. Book a demo to see it in action.
How Bank Bots Support Banking Teams Across Functions
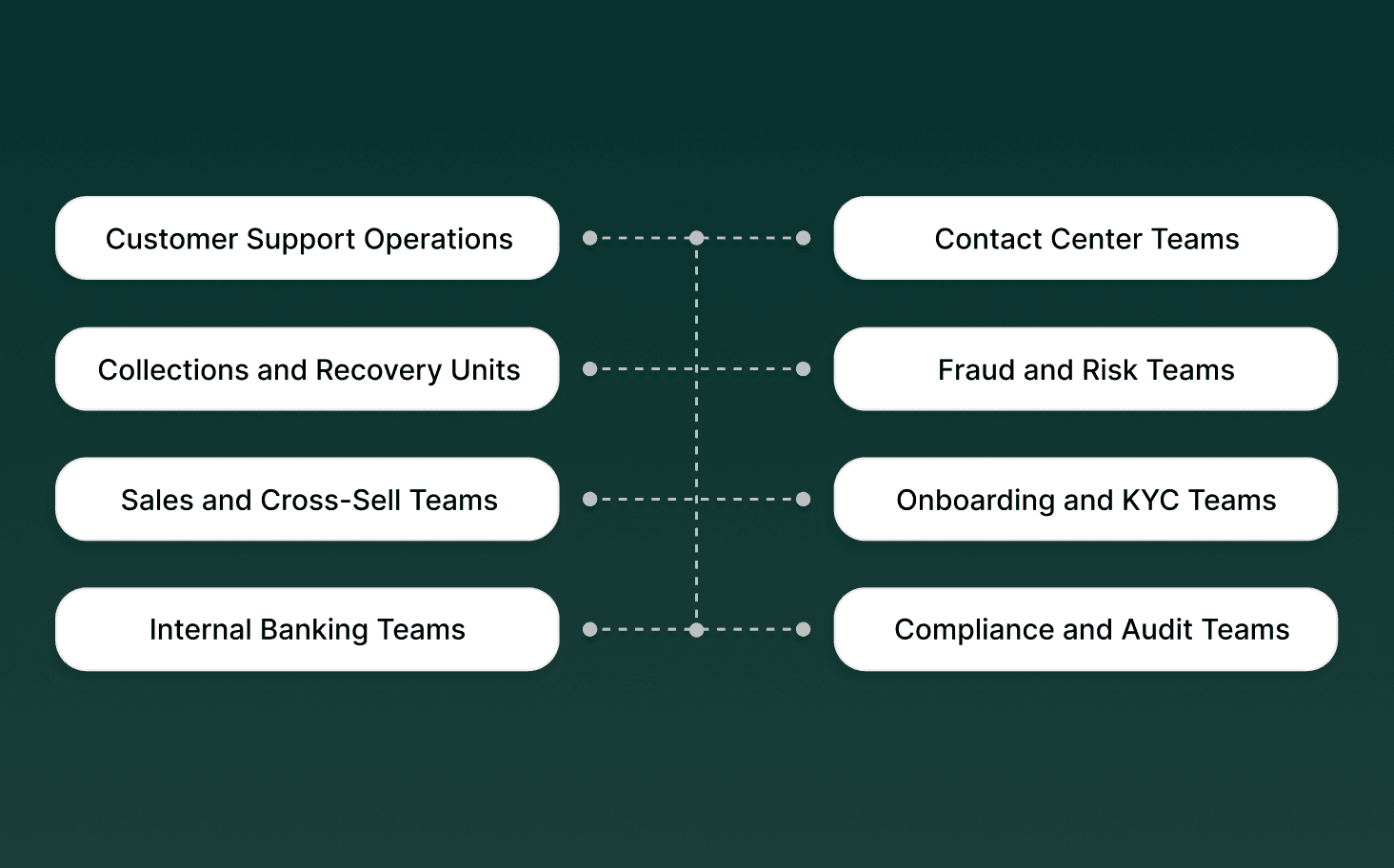
Bank bots support banking teams by taking over high-volume, rules-based work while keeping humans responsible for judgment-heavy and regulated decisions. Each function uses bots differently based on risk level and workflow complexity.
Customer Support Operations: Bots resolve balance checks, transaction queries, card status, and branch information, reducing inbound ticket and call load.
Contact Center Teams: Bots absorb peak-hour traffic, shorten wait times, and route verified customers to the right agent queue.
Collections and Recovery Units: Bots handle payment reminders, due-date confirmations, and settlement prompts using predefined scripts and escalation rules.
Fraud and Risk Teams: Bots gather preliminary information, guide customers through blocking cards, and route cases to analysts with complete context.
Sales and Cross-Sell Teams: Bots qualify leads, confirm interest, and schedule follow-ups without altering product terms or pricing.
Onboarding and KYC Teams: Bots guide users through document submission steps and status checks while final verification remains manual.
Internal Banking Teams: Bots answer employee queries related to SOPs, policy lookups, and system navigation.
Compliance and Audit Teams: Bots create detailed logs of every interaction, supporting traceability and post-call review.
Bank bots support teams by removing operational noise, preserving compliance, and allowing specialists to focus on decisions that require judgment, verification, and accountability.
Key Trends Shaping Bank Bots and Banking AI Chatbots
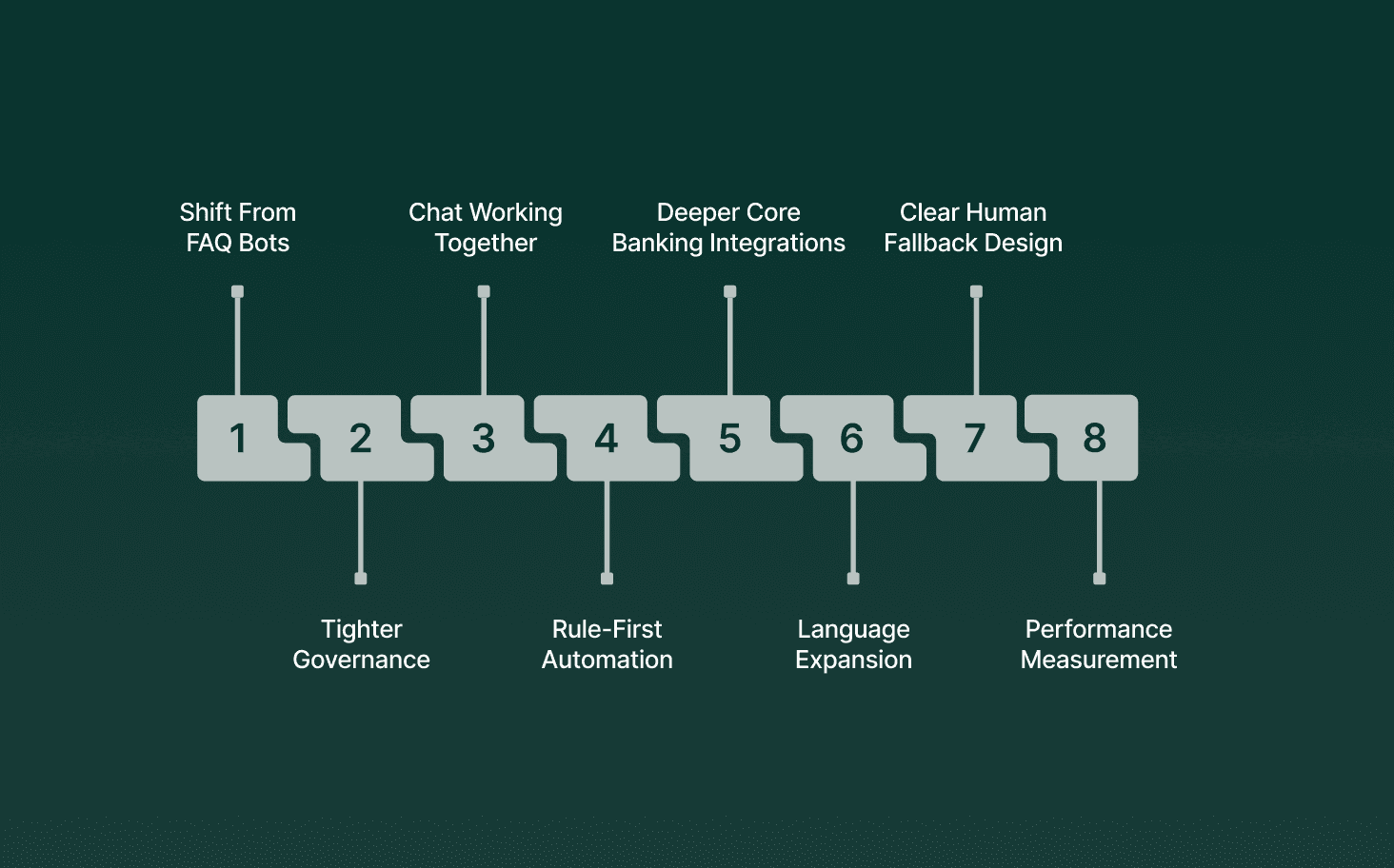
Bank bots and banking AI chatbots are evolving in response to regulatory scrutiny, rising service volumes, and the need for predictable automation. Trends focus on control, reliability, and measurable outcomes rather than broad experimentation.
Shift From FAQ Bots to Transactional Bots: Banks prioritize bots that complete actions such as balance checks, card blocks, and payment scheduling instead of only answering questions.
Tighter Governance and Auditability: Bot workflows include approval logic, interaction logs, and review trails aligned with internal risk and audit teams.
Voice and Chat Working Together: Banks link voice bank bots and banking AI chatbots so customers can move across channels without repeating information.
Rule-First Automation With AI Assistance: Deterministic rules handle regulated steps, with AI used for intent detection and routing rather than free-form responses.
Deeper Core Banking Integrations: Bots connect directly to account systems, payment rails, and CRMs to provide real-time status updates.
Language Expansion for Regional Coverage: Multilingual bots address regional language needs without duplicating agent teams.
Clear Human Fallback Design: Bots are built with defined thresholds for escalation to agents based on confidence, risk, or customer intent.
Performance Measurement Beyond CSAT: Banks track containment rate, resolution time, escalation accuracy, and compliance adherence.
Current trends show banks building bank bots and banking AI chatbots that operate within strict boundaries, support multiple channels, and deliver measurable operational impact without increasing risk.
How Smallest.ai Supports Production-Ready Bank Bots
Smallest.ai is built for banks that need voice bank bots to perform reliably under real operational pressure. The platform focuses on real-time execution, controlled workflows, and enterprise deployment models rather than demo-only capabilities.
Real-Time Voice Agents for Live Calls: Smallest.ai voice agents transcribe, reason, and respond during live phone calls, making them suitable for high-volume inbound and outbound banking use cases.
Low-Latency Speech Generation: Speech is generated in under 100 ms, which keeps conversations natural and avoids awkward pauses that break customer trust.
Strong Handling of Numbers and Entities: Voice models accurately process sensitive data such as card numbers, account references, OTPs, and phone numbers during calls.
Scalable Concurrent Call Handling: Agents manage thousands of parallel calls per day without performance drop-offs, supporting peak banking traffic.
On-Premise and Controlled Deployments: Banks can deploy models on their own infrastructure, keeping inference and customer data within approved environments.
Multilingual Voice Coverage: Support for 16+ languages allows banks to serve regional customers without duplicating agent teams.
Developer SDKs and System Integration: Python, Node, and REST APIs make it easier to connect bank bots with telephony, CRMs, and core banking systems.
Built-In Compliance Readiness: Enterprise security standards, including SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, PCI, and ISO, support regulated banking operations.
For banks moving from pilots to production, voice reliability and deployment control matter more than novelty. Smallest.ai provides the infrastructure needed to run bank bots at scale without compromising performance, security, or compliance.
Final Thoughts!
Bank bots have settled into a clear role inside modern banking teams. They handle defined workloads, operate within strict boundaries, and support measurable outcomes across service, risk, and operations. What matters now is execution. The difference between a useful deployment and a frustrating one comes down to latency, accuracy, language handling, and how reliably the bot performs under real call volumes.
That is where purpose-built voice infrastructure becomes critical. Platforms like Smallest.ai focus on real-time voice agents designed for regulated environments, high concurrency, and predictable performance at scale.
If your team is evaluating voice-led bank bots or banking AI chatbots for production use, explore how Smallest.ai supports enterprise-grade deployments. Book a demo to see how real-time voice agents operate in live banking workflows.

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now