See how AI voice technology supports real operations, improves accuracy, and scales complex workflows. Learn where voice AI delivers meaningful business impact.

Kaushal Choudhary
Updated on
February 24, 2026 at 8:57 AM

When teams start exploring AI voice technology, it’s usually because something in their customer experience isn’t working the way it should. Maybe support calls are piling up, agents are repeating the same answers all day, or customers just wish they could get simple tasks done without having to wait on hold.
It’s a relatable moment; technology feels like it should solve it, but the path forward isn’t always obvious.
Voice interaction isn’t niche anymore. As of 2025, about 20.5% of people worldwide use voice search or voice assistants in their interactions with technology, a clear sign that voice-first interfaces are becoming routine in digital behavior across markets.
In this guide, we’ll take you through what AI voice technology actually involves, where it delivers real value, and what you need to consider before adopting it in your operations.
Key Takeaways
Voice AI Depends on Multiple Coordinated Systems: AI voice performance relies on acoustic processing, ASR, NLU, dialog state tracking, and low-latency TTS operating together in real time.
Training Requires Detailed Audio–Text Alignment: High-quality datasets, phoneme-level timing, prosody modeling, and model compression create responsive voice systems suitable for enterprise workloads.
Enterprises Use Voice AI for Structured Operations: Contact centers, sales teams, verification workflows, and scheduling functions depend on voice AI to execute predictable, rule-based processes at scale.
Real-World Conditions Create Reliability Challenges: Latency spikes, noise, accent variability, backend delays, and compliance constraints directly impact performance in production environments.
Smallest.ai Delivers Enterprise-Grade Control and Scale: On-premise inference, multilingual models, high concurrency, strict SOP adherence, and SOC 2/HIPAA security make it suitable for large operational teams.
Core Components of AI Voice Technology
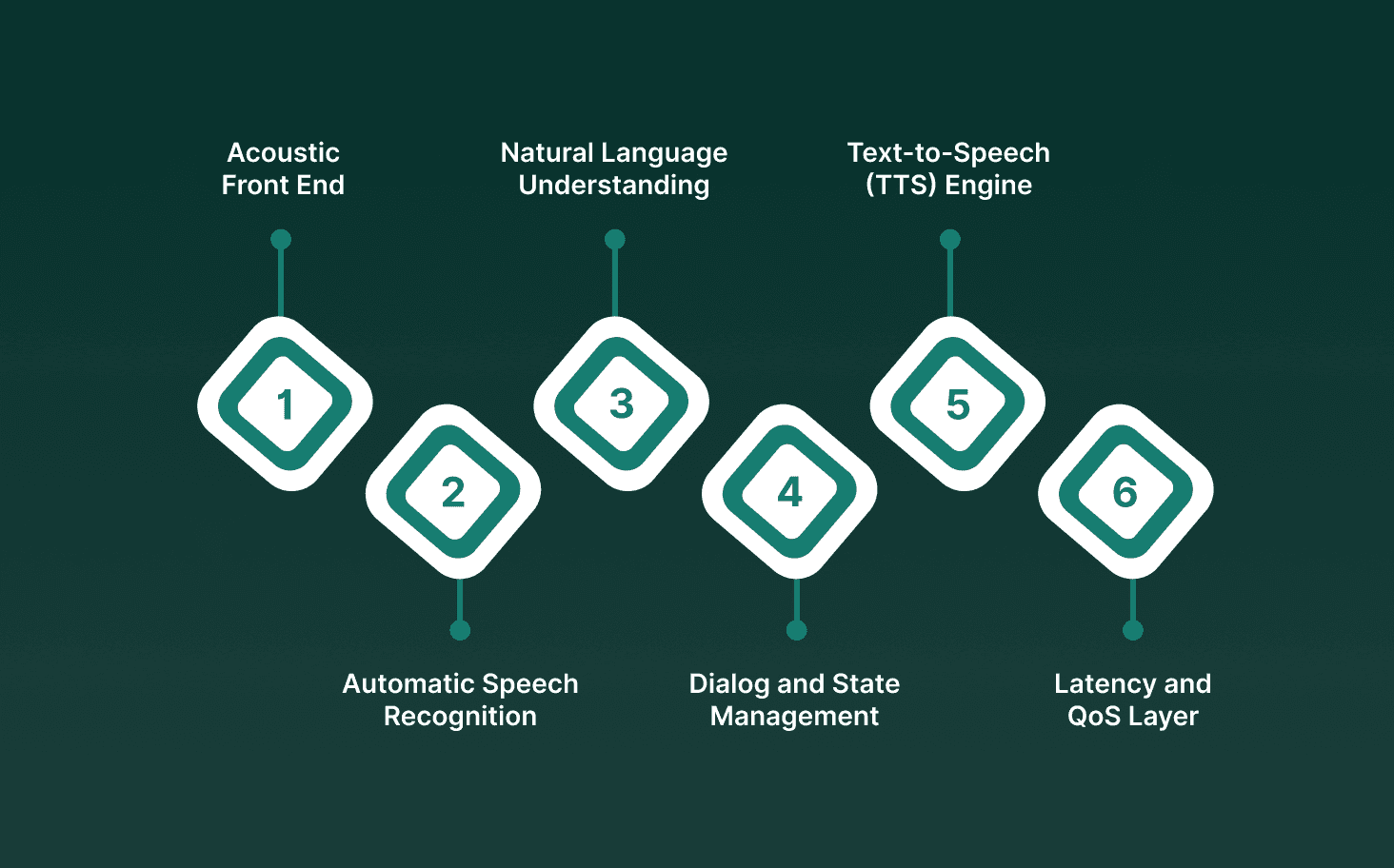
AI voice technology brings together several tightly linked systems that process audio, predict text, generate speech, and maintain context in real time. Each component must operate with low latency and high accuracy for voice-based AI to function reliably in enterprise environments such as contact centers, automated operations, and multilingual service pipelines.
Acoustic Front End: Converts raw waveforms into machine-readable features. Extracts spectrograms and mel-frequency coefficients that capture pitch, tone, and energy patterns needed for downstream models.
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): Transcribes speech into structured text. Uses transformer-based architectures optimized for streaming inference, producing tokens in sub-200 ms windows for real-time interaction.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Interprets intent and domain context. Maps the ASR output to intents, entities, and domain labels, allowing systems to run workflows such as authentication, routing, or transaction handling.
Dialog and State Management: Maintains conversation flow. Tracks session state, previous turns, and backend results to avoid repetition, interruptions, or conflicting responses during long calls.
Text-to-Speech (TTS) Engine: Generates human-like speech at low latency. Uses neural vocoders and diffusion or autoregressive models tuned for interactive workloads, keeping end-to-end response time under one second.
Latency and QoS Layer: Guarantees stable performance under traffic spikes. Monitors jitter, packet loss, and GPU queue lengths to keep interaction smooth even when calls scale into thousands.
This foundation allows AI voice technology to conduct real-time voice interaction AI at an enterprise scale while maintaining clarity, speed, and consistency.
For a clearer view of how today’s voice systems function, continue with Understanding What Voice Cloning Is and How It Works
How AI Voice Models Are Trained
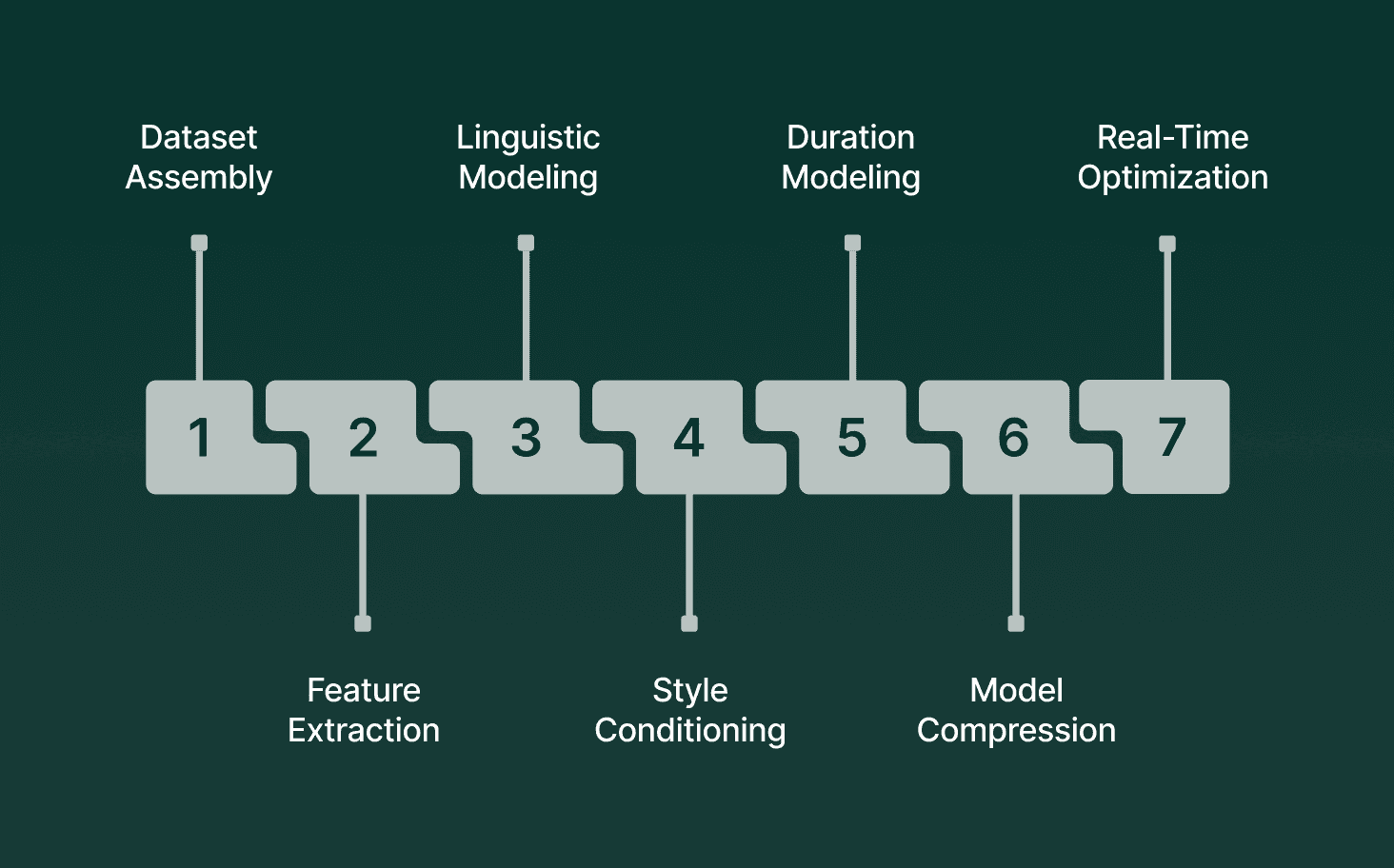
Training AI voice models involves multiple data pipelines and optimization steps designed to achieve low-latency inference, natural prosody, and domain accuracy. Each stage focuses on a different part of the audio-text relationship, from raw waveform processing to final model distillation for real-time workloads.
Dataset Assembly: Curated audio–text pairs across accents, noise levels, and speaking styles. Includes studio-grade recordings, conversational datasets, and domain-specific corpora. For TTS, speech is paired with normalized transcripts; for ASR, datasets include overlapped speech, variable mic quality, and multi-speaker samples.
Preprocessing and Feature Extraction: Conversion of raw audio into stable training features. Generates mel-spectrograms, phoneme alignments, pitch curves, and energy contours that help the model learn pronunciation, rhythm, and emphasis patterns.
Acoustic and Linguistic Modeling: Training transformer or conformer networks on long audio sequences. ASR models learn token probabilities over time; TTS models learn duration, pitch, and prosody prediction. Multi-head attention helps capture long-range dependencies for natural pacing and clarity.
Speaker and Style Conditioning: Encoding attributes like identity, accent, emotional tone, and speaking rate. Embedding vectors allow the model to reproduce consistent voice characteristics or switch styles without retraining.
Alignment and Duration Modeling: Mapping phonemes to precise time intervals. Critical for TTS, where duration errors cause unnatural pacing. Forced aligners or learned duration models synchronize text and audio frames at millisecond resolution.
Model Compression and Distillation: Reducing model size while preserving audio fidelity. Techniques like quantization, pruning, and student-teacher distillation bring inference latency under the thresholds required for interactive systems.
Real-Time Optimization: Benchmarking and fine-tuning for streaming inference guarantees models produce partial outputs incrementally, allowing responses within sub-second budgets for voice interactive AI.
Collectively, these training steps create voice models that respond quickly, maintain clarity across languages and domains, and support consistent behavior in production environments.
Enterprise Use Cases of AI Voice Technology Across Industries
AI voice technology supports operational workloads where accuracy, speed, and workflow execution matter more than novelty. Enterprises use voice-based AI to handle structured tasks, reduce manual intervention, and maintain service consistency across high-volume environments.
1. Debt Collection
AI voice agents simplify the delicate process of debt recovery by automating outreach and negotiation. These systems can manage high volumes of calls while adhering to strict compliance standards, making sure that collections are handled efficiently without damaging customer relationships.
24/7 Availability: Agents can contact debtors at optimal times outside of standard business hours to deliver timely payment reminders and facilitate immediate resolution.
Build Debtor Trust: The AI maintains a firm yet empathetic and respectful tone throughout the interaction, guaranteeing a smooth experience that preserves the customer's dignity and trust.
Take Real Actions: Beyond simple reminders, the system can effectively negotiate payment terms, confirm promises to pay, and instantly update CRM systems to reflect the latest interaction data.
2. E-Commerce
In the competitive e-commerce landscape, AI voice agents act as always-on sales and support associates. They help recover revenue from abandoned interactions and provide instant support, turning potential friction points into sales opportunities and improved brand loyalty.
Drive Conversions: Agents proactively engage customers to follow up on abandoned carts, recommend relevant products, and automatically update order statuses to boost sales figures.
Build Shopper Trust: By delivering personalized, helpful experiences that feel human, the AI fosters trust and loyalty even when handling thousands of simultaneous customer requests.
Escalate To Humans: The system intelligently identifies high-touch or complex queries and smoothly switches the call to a human agent, providing zero friction in the buyer's journey.
3. Logistics
Logistics operations benefit from AI voice technology through improved communication flow between dispatchers, drivers, and customers. These agents automate the tracking and verification process, reducing the manual workload on support teams and preventing costly delivery failures.
Address Verification: Before dispatch, AI agents proactively call or message customers to confirm delivery addresses, significantly reducing the rate of failed deliveries and return logistics costs.
Real-Time Updates: The system fields routine inquiries regarding route updates, delay notices, and tracking requests, effectively reducing the pressure on human dispatch teams.
Simplify Operations: Agents integrate directly with backend systems to confirm deliveries, update Estimated Times of Arrival (ETAs), and log issues instantly for better operational visibility.
4. Healthcare
AI voice agents in healthcare alleviate administrative burdens by managing patient engagement and routine communications. This allows medical staff to focus on patient care while guaranteeing that appointments, billing, and follow-ups are handled securely and compassionately.
Compassionate Support: The AI provides empathetic, human-like interaction for appointment bookings and post-care queries, guaranteeing communication is both comforting and compliant with health regulations.
System Integration: Agents integrate smoothly with Electronic Health Records (EHR) to automate scheduling, appointment reminders, and prescription refills securely in real-time.
Instant Call Routing: To guarantee patient safety and efficiency, the system automatically assesses needs and routes patients to the appropriate medical team based on urgency.
5. Customer Service
For businesses of all sizes, missed calls often mean lost revenue. AI voice agents serve as a reliable first line of defense, managing bookings, inquiries, and support tasks around the clock to make sure that every customer interaction is captured and resolved.
Automate Busywork: The AI handles repetitive administrative tasks such as confirming appointments, logging payments, and sending invoices, freeing up staff to focus on complex issues.
Build Customer Loyalty: By offering fast, friendly responses that reflect the brand's unique personality, the AI guarantees customers feel valued and heard at every touchpoint.
Smart Handoff: When a situation requires human nuance, the AI routes the conversation smoothly to a live staff member, maintaining a continuous and professional service experience.
6. Real Estate
In real estate, speed is often the deciding factor in closing a deal. AI voice agents act as immediate lead qualifiers, engaging potential buyers the moment interest is shown to schedule viewings and answer questions before competitors can respond.
Capture Every Opportunity: With 24/7 capability, agents respond immediately to inquiries from buyers and sellers, making sure that no lead is lost due to after-hours delays.
Qualify And Negotiate: The AI is capable of negotiating and qualifying leads with intelligence and finesse, customized to specific property details and seller requirements.
Move Deals Faster: By automating the scheduling of property showings and managing follow-up communications, the system simplifies the path from initial inquiry to closed deal.
7. Recruitment
Recruitment teams use AI voice agents to automate the time-consuming initial stages of hiring. By handling screening and scheduling, these agents allow recruiters to spend their time building relationships with top candidates rather than managing logistics.
Instant Candidate Engagement: The AI screens resumes and responds to applicants immediately, keeping the hiring funnel active and preventing top talent from losing interest.
Build Candidate Trust: Candidates receive thoughtful, quick responses that reflect the company's culture, eliminating the frustration of "ghosting" and confusion during the application process.
Automate Hiring Tasks: The system automatically schedules interviews, sends required assessments, and logs all updates directly into the Applicant Tracking System (ATS) without manual input.
See how Smallest.ai delivers real-time voice automation with on-premise control, multilingual accuracy, and reliable workflow execution. Start your demo today.
Challenges Within Modern AI Voice Systems
Modern AI voice systems operate under strict latency, accuracy, and reliability constraints, especially in enterprise environments where calls trigger transactions, authentication steps, or regulatory processes. These challenges arise from real-world conditions that differ significantly from controlled training datasets.
Challenge | What It Causes |
Latency Under Load | GPU queueing or network jitter adds 150–200 ms, breaking conversational flow and barge-in handling. |
Noise & Overlapping Speech | ASR accuracy drops when background noise masks phonemes or when callers self-interrupt. |
Accent & Dialect Variability | Higher substitution/deletion errors due to the limited representation of region-specific speech patterns. |
Context Drift in Long Calls | Loss of prior steps or answers during workflows that run for ten minutes or more. |
Backend Dependency | Slow CRM or billing systems create long pauses that sound like model failures. |
Security & Compliance Constraints | Need for encrypted streams, selective recording, and real-time PII redaction. |
Model Hallucination Risks | Unapproved or incorrect instructions if workflows lack strict guardrails and domain grounding. |
Enterprises solve these challenges with optimized models, workflow constraints, and infrastructure tuned for real-time operations.
For teams exploring advanced voice capabilities, continue with Creating An AI Voice With A Generator
Future Directions and Ethical Considerations in AI Voice Technology
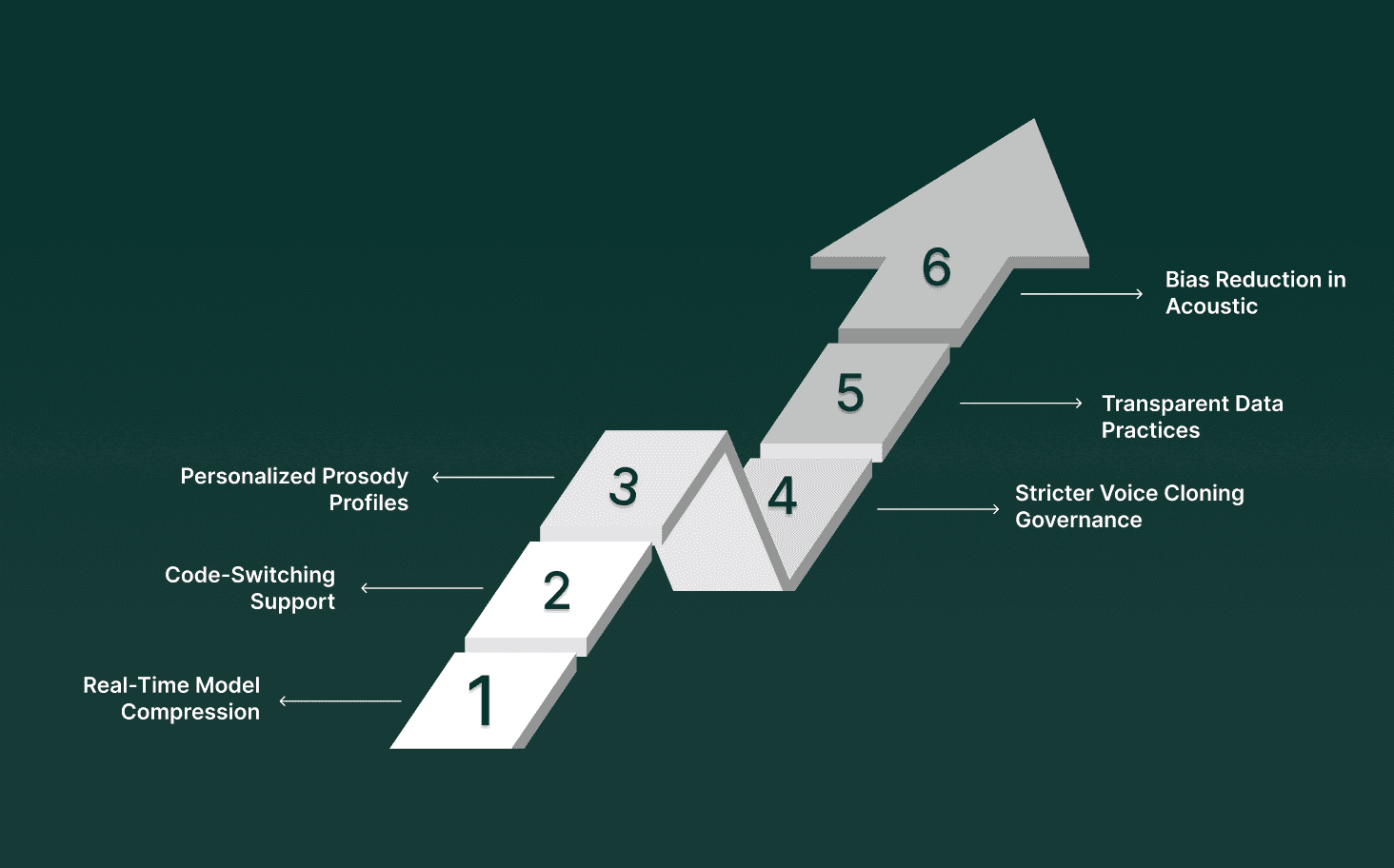
AI voice technology is advancing toward higher fidelity, lower latency, and tighter enterprise integration. These improvements bring new engineering priorities, along with ethical frameworks that govern how voice systems operate in regulated and consumer-facing environments.
Real-Time Model Compression: Smaller architectures optimized for sub-100 ms inference. Compression methods reduce model size, lower GPU demand, and allow faster token generation while keeping prosody stable during live interactions.
Cross-Lingual and Code-Switching Support: Models that handle multilingual calls without switching engines. Enterprises need ASR and TTS systems that maintain accuracy across blended speech patterns, especially in regions where callers shift languages mid-sentence.
Personalized Prosody Profiles: Voice output that adapts to user context and task type. Future TTS engines adjust tone, pacing, and clarity based on interaction patterns, caller state, or domain rules while maintaining policy compliance.
Stricter Voice Cloning Governance: Guardrails around identity verification and clone authorization. Systems require explicit consent flows, watermarking, and detection protocols to prevent misuse of synthetic voices for impersonation or fraud.
Transparent Data Practices: Clear handling of audio logs, retention periods, and redaction. Enterprises must specify what is recorded, what is transcribed, and what is deleted, avoiding hidden data usage or opaque training pipelines.
Bias Reduction in Acoustic and Linguistic Models: Targeted tuning for underrepresented accents. Addressing phoneme-level error disparities reduces unequal treatment in support, verification, or automated dispute flows.
These future directions reflect a shift toward high-performance voice systems that remain accountable, secure, and trustworthy as their capabilities expand.
How Smallest.ai Powers Real-Time, Enterprise-Grade Voice AI
Smallest.ai supports enterprises that need predictable, low-latency voice automation across high-volume calls, strict workflows, and regulated data environments. Its platform combines real-time speech systems, on-premise deployment, multilingual support, and developer tooling in a single operational stack.
On-Premise Deployment With Hardware Control: Runs models directly on enterprise servers. Let's organizations own inference, reduce external latency, meet residency rules, and deploy voice agents on custom or high-security infrastructure.
Workflow Reliability for Complex SOPs: Executes hundreds of conditional paths without drift. Agents follow structured logic, maintain call state, and consistently resolve edge cases, supporting industries that cannot tolerate deviations.
High-Concurrency Call Handling: Manages thousands of inbound or outbound calls simultaneously. Works through the Smallest.ai platform or enterprise telephony integrations, keeping performance stable during peak demand.
Multilingual, High-Precision Voice Models: Accurate with numbers and consistent across 16+ global languages. Supports credit card numbers, policy IDs, phone numbers, and context-heavy phrases, and enables service across four continents.
Developer SDKs With Deep Integration Support: Python, Node.js, and REST APIs for full system embedding. Allows agents to read and write data inside CRMs, logistics tools, healthcare systems, and custom operational software.
Enterprise Security and Auditable Insights: SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and PCI alignment with analytics dashboards. Protects sensitive information while giving teams access to call logs, transcripts, and behavior metrics for review and refinement.
Smallest.ai brings the predictability, speed, and operational control required for real-time voice automation across large, complex enterprise environments.
Final Thoughts!
Adopting AI voice technology is not only about automating conversations. It reshapes how teams think about capacity, accuracy, and the level of consistency they can deliver across every phone interaction. As organizations move from experimentation to real operational use, the gap widens between generic voice tools and platforms built for sustained, high-volume performance. That’s where the real long-term value of AI voice technology becomes clear, not in novelty, but in its ability to support the day-to-day work that keeps a business running.
If you’re aiming for real-time performance, multilingual coverage, predictable workflows, and deployment models that meet enterprise requirements, Smallest.ai gives your team the control and precision needed to make voice automation reliable at scale.
Talk to a voice expert today and see how Smallest.ai fits your operations.
Answer to all your questions
Have more questions? Contact our sales team to get the answer you’re looking for

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now


