Explore what is conversational AI through real-world examples in answering queries, booking, and managing orders. Enhance interactions now!

Prithvi Bharadwaj
Updated on
December 26, 2025 at 11:28 AM

Conversational AI vs. Generative AI: What Sets Them Apart
AI has introduced a transformative era for businesses. Through seamless human-machine collaboration, AI aims to enhance efficiency and personalization. Two key technologies, conversational AI and generative AI, are at the forefront of this digital revolution.
The influence of AI on client engagement, marketing, content creation, and customer service is undeniable, as highlighted by Gartner's projections:
By 2025, AI will generate 30% of all outbound marketing messages.
It's predicted that by 2027, 50% of the generative AI models businesses rely on will be tailor made to a particular industry or job role.
Conversational AI and generative AI are essential for making interactions feel more human and personalized, but they have different jobs. At first glance, they seem alike, but they are used differently, trained differently, and produce different results. If you don't recognize these differences, you might pick the wrong tool and not get as much value.
This article focuses on the main differences between conversational AI and generative AI, exploring what makes each one special, their challenges, and how they can work together.
What is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI refers to systems that can simulate human-like conversations through text or speech. These systems are capable of understanding user input, processing context, and delivering meaningful responses across multiple channels, languages, and platforms.
Unlike traditional rule-based bots that only respond to specific keywords, conversational AI is powered by advanced machine learning algorithms. This enables it to:
Understand context and intent
Personalize responses in real time
Handle multi-turn conversations
Escalate complex queries to human agents when needed
This technology is widely used across industries — from customer service chatbots to intelligent voice assistants and AI copilots integrated into business workflows.
The Technology Behind Conversational AI (How It Works?)
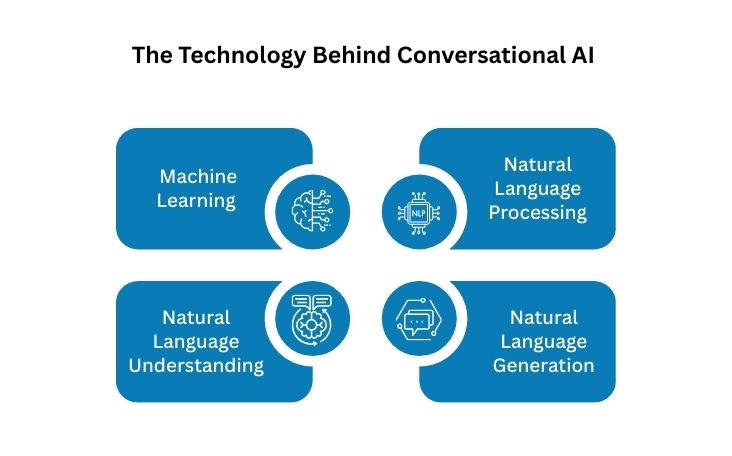
Conversational AI operates through a combination of several core technologies that allow it to process and respond to human input effectively:
1. Machine Learning (ML)
The first is Machine Learning (ML), a branch of AI that uses complex algorithms and statistical models to identify patterns in massive data sets and make predictions. ML is crucial for any conversation AI engine that wants to chat with people. It allows the AI to become more intelligent by learning from the information it collects, improving its understanding and ability to answer questions.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) is the latest technique for examining language using machine learning in conversational AI. Previously, the development of language processing methods progressed from linguistics to computational linguistics and then to statistical natural language processing.
The process involves four key steps:
Input Generation: Users interact through a website or app, providing input in either text or voice format.
Input Analysis: Natural Language Understanding (NLU) interprets meaning and intent if the input is text-based. A combination of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and NLU processes the data for voice inputs.
Dialogue Management: The AI decides how to respond.
Response Generation: Natural Language Generation (NLG) creates a human-like reply.
Reinforcement Learning: Machine learning models refine and optimize reactions over time to improve accuracy and effectiveness.
3. Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
NLU helps the AI understand the meaning behind the words, identifying context, sentiment, and even user frustration. It’s what enables AI to distinguish between “I’m cold” (weather complaint) and “I got the cold shoulder” (social experience).
Also Read: Speech-to-Text and Text-to-Speech Technology: Making Interactions Smarter
4. Natural Language Generation (NLG)
After understanding the user's input, the system formulates a coherent and contextually appropriate response. Natural language generation (NLG) enables virtual agents to construct humanlike sentences in a clear, relevant, and linguistically natural manner. NLG uses powerful deep learning algorithms to formulate responses in context. Moreover, as AI chatbots interact more with users and human agents, these responses become more sophisticated and conversational.
As we have understood what conversational AI is and how it works? Now, let's examine the types that are part of conventional AI.
Real-World Use Cases of Conversational AI
Conversational AI takes many forms, each designed to simulate human interaction and drive better engagement, automation, and efficiency. Here’s a look at the primary types of conversational AI, along with real-world examples showing how businesses and users benefit today.
1. AI Chatbots (Text-Based Customer Support & Engagement)
Modern AI chatbots are no longer rule-based, limited-response bots. They use large language models (LLMs) to understand context, sentiment, and user intent, making them capable of handling complex, multi-turn conversations with relevance and empathy.
🔍 Use Cases:
Customer Support: Automating FAQs, returns, or billing inquiries.
Lead Qualification: Engaging visitors on websites and collecting pre-sales information.
Content Generation: Assisting users with summaries, writing help, or creative prompts.
Examples:
OpenAI ChatGPT: Powers interactive help desks, knowledge assistants, and even creative tools across industries.
Google Gemini: Enables multimedia query handling, suitable for educational platforms and advanced content creation.
Microsoft Bing Chat: Enhances search with conversational experiences, complete with cited sources.
Chatbots are widely adopted in banking, retail, education, and B2B platforms to reduce support costs and scale personalization.
Want to learn more about chatbots? Click here.
2. Interactive Voice Assistants (IVAs)
IVAs leverage natural language processing and voice recognition to engage users through spoken commands. These assistants are prevalent in both consumer electronics and enterprise-grade systems.
Use Cases:
Smart Homes: Voice-activated control of lighting, music, and appliances.
Healthcare: Assisting patients with appointment scheduling or medication reminders.
Accessibility: Empowering visually impaired users through hands-free interaction.
Examples:
Amazon Alexa: Used in smart homes and retail kiosks.
Apple Siri: Embedded in Apple devices to perform personal tasks.
Google Assistant: Powers voice search, navigation, and connected device control.
IVAs are increasingly used in IoT ecosystems, providing seamless voice interfaces for consumer and industrial applications alike.
Readers Also Liked: How to Make Alexa Text-to-Speech Voice Online
3. AI Copilots (Productivity & Decision Support Tools)
AI copilots act as intelligent workplace assistants, embedded in tools like CRMs, code editors, and collaboration platforms. These assistants streamline complex workflows and support decision-making in real time.
Use Cases:
Code Assistance: Suggesting or auto-generating code blocks for developers.
Document Automation: Drafting emails, proposals, and reports based on brief prompts.
Data Analysis: Pulling insights from structured or unstructured data via natural language queries.
Examples:
GitHub Copilot: Used by developers for live code generation.
Salesforce Einstein: Automates CRM tasks like lead scoring and forecasting.
Microsoft 365 Copilot: Assists users across Excel, Word, and Teams.
These assistants are commonly used in tech, finance, and operations roles where reducing cognitive load and time-to-output is a priority.
4. Domain-Specific Conversational AI (Vertical Solutions)
Some conversational AI tools are purpose-built for specialized industries or tasks, with knowledge bases and capabilities tailored to unique user needs.
Use Cases:
Healthcare: Virtual nurses triaging patient symptoms or answering health queries.
Education: AI tutors offering real-time feedback or study assistance.
Retail: In-store or e-commerce bots helping with product discovery and purchases.
HR: Screening candidates or answering policy-related employee questions.
These bots drive operational efficiency and personalize user experiences within highly regulated or customer-centric industries.
What are the Benefits and Challenges of Conversational AI?
Conversational AI is growing and providing advantages to a wide array of businesses. Companies in numerous sectors, including those listed below, can use conversational AI in a variety of situations and enjoy its advantages:
Healthcare
Conversational AI can help patients describe their conditions online by asking questions to shorten wait times.
Patient Assistance: AI-powered chat systems help schedule appointments, answer medical inquiries, and assess symptoms. They guide patients through treatment options and streamline access to healthcare services.
Mental Health Support: Emotionally intelligent virtual assistants provide therapeutic conversations, stress management techniques, and coping strategies to support mental well-being.
Clinical Support: In medical environments, AI enhances efficiency by handling administrative tasks, organizing patient data, and assisting healthcare professionals with informed decision-making.
Banking
Inefficient traditional chatbots can leave customers frustrated. Instead, banks can leverage AI chatbots to manage complex inquiries effectively. Given the sensitivity of financial matters, ensuring accuracy and minimizing human errors is essential for providing precise responses and addressing customer concerns.
Retail
Even when customer service agents are off the clock, AI-powered chatbots can be available 24/7, including on holidays. Previously, we connected only with customers through call centers or face-to-face, but that's changed. Thanks to AI chatbots, customer support isn't stuck within regular business hours. These chatbots can reach customers anywhere through email or a company's website.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Amazon Alexa and Apple Siri, which are found on everyday gadgets, let you use conversational AI. Smart home devices also have this kind of AI built right in.
Human Resources
Conversational AI can take over the tedious HR task of manually reviewing job applicants' qualifications during the hiring process.
Accessibility Features
Conversational AI can improve user accessibility by providing voice-activated assistance for those with disabilities. For example, individuals with visual impairments or mobility challenges can use voice-enabled controls more accurately using natural speech.
Now, if you are a developer or an organization wanting to implement conversational AI, you must also consider some common challenges that are involved, such as the following:
Language Translation
Until now, many chatbot AI have been trained mainly in English, leaving people who don't speak English out in the cold when interacting in their languages. For businesses that operate worldwide, though, multilingual chatbots owned by specific companies are a good choice for handling customer service.
Privacy and Security
Because conversational AI relies on gathering data to respond to user questions, it's also at risk of privacy and security problems. Building conversational AI applications with strong privacy and security measures and adequate monitoring will foster trust among users. It is where Waves and Atom by Smallest.ai put additional emphasis on data protection. Try out Waves for free today and see the change in your chatbot adoption in the long run.
Ethical and Regulatory Compliance
Conversational AI solutions face another hurdle, particularly in heavily regulated healthcare and banking. When customer data is mishandled, or compliance rules are broken during or after conversations, it shakes customer confidence and can seriously damage a brand's reputation, sometimes beyond repair. Even worse, this can spiral into a major public relations disaster and cause the loss of potential business.
Difficulty Interpreting Certain Words and Contexts
Slang, jargon, and regional dialects can throw off conversational AI. These are all examples of human languages' changing nature. Developers are working on training the technology to overcome these challenges.
Biased Outputs
If a conversational AI is trained on a limited dataset, it might generate biased responses. For instance, if the training data isn't diverse enough, the AI system might struggle to comprehend certain accents or could provide inaccurate information.
Grasping conversational AI's benefits and challenges provides valuable insight into its capabilities and limitations. Now, let's explore generative AI and understand how it works, its unique advantages, and the challenges it presents.
What is Generative AI (GenAI)?
Generative AI (GenAI) is a sophisticated type of artificial intelligence that harnesses the power of deep learning to create new content that's both original and relevant. This content can span various formats, such as text, images, video and audio clips, code, and even product designs. As a relatively recent development in the tech world, GenAI is constantly giving rise to fresh and exciting applications, particularly in content creation and creative services. It covers a bunch of things, like:
Adding more content
Automatically creating summaries
Changing the text and its tone
Sorting things into categories
Making things simpler
GenAI will have a lasting effect and open up new possibilities for creating code, designing products, and updating old code. AI-generated data can fill gaps where there is little data, keep sensitive information private, and help reduce bias.
Also Read: What is Text-to-Speech
Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI can offer brands multiple benefits, such as boosting revenue, fostering stronger customer loyalty, and giving them an advantage over the competition. Let's examine each of these benefits one by one.
GenAI Enhances Creativity
This tool comes up with fresh concepts and methods. Breaking new ground regarding imagination and ingenuity, helping companies stand out with a one-of-a-kind and unforgettable image.
GenAI Boosts Customer Experience
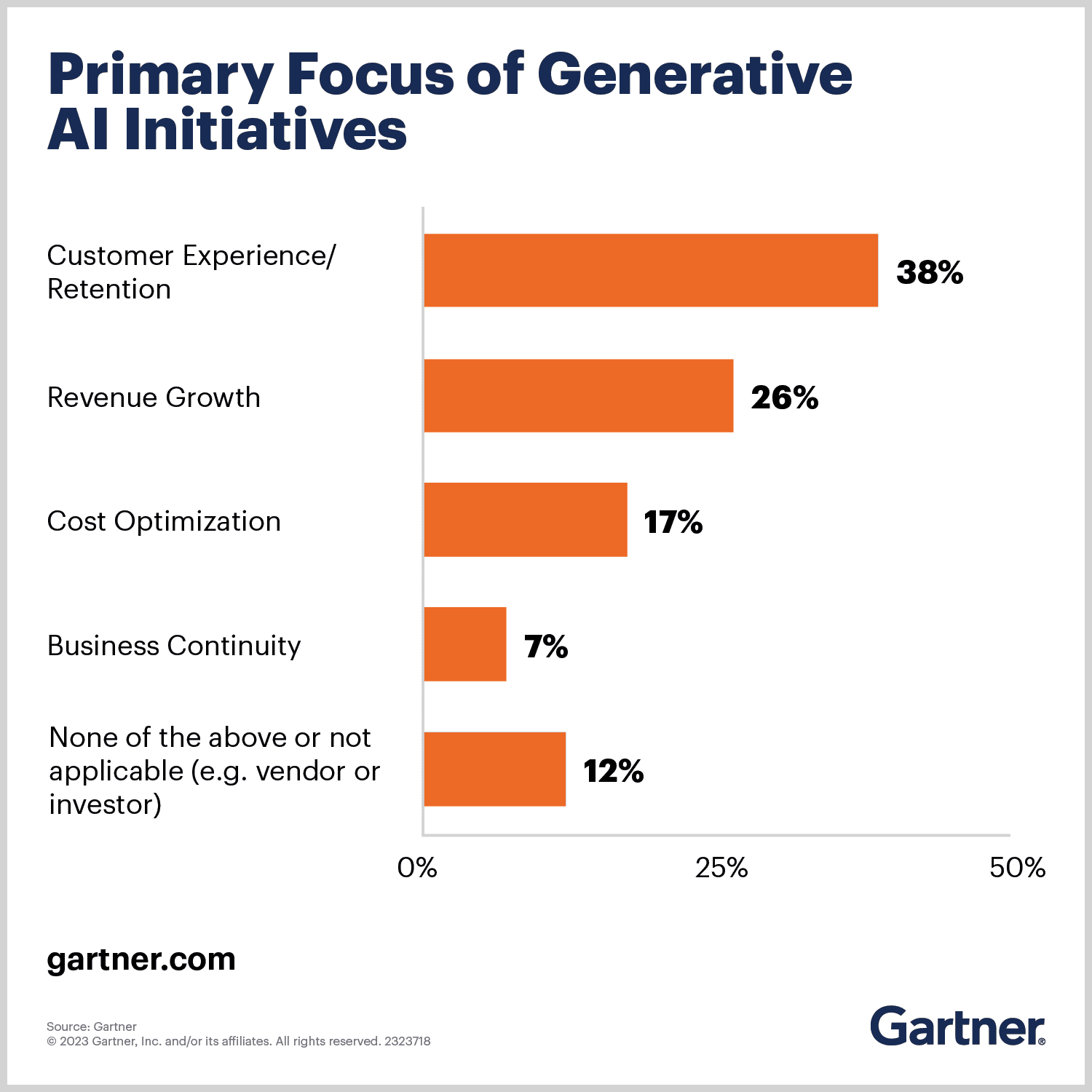
The technology turns everyday interactions between customers and the brand into stand-out moments by cleverly tailoring the content and aiming it precisely at what people like. According to Gartner, 38% of business leaders bank on GenAI to optimize customer experience.
GenAI Uncovers Revenue Opportunities.
GenAI empowers brands to innovate on a grand scale, uncovering fresh concepts, unique flavors, energy-saving devices, natural medicines, and beyond. Organizations with AI maturity can extract the most value from the technology.
GenAI Multiplies Cost Savings and Productivity.
Generative AI enables businesses to cut expenses and enhance efficiency by augmenting employees, refining processes, and identifying long-term talent. For example, integrating genAI into customer support allows representatives to streamline problem-solving and adjust their communication styles to suit each situation.
Challenges and Risks
ChatGPT and similar AI tools leverage data from the public domain to gain insights and tailor their responses. Unfortunately, this approach has resulted in problems like deepfakes and violations of intellectual property rights, which are as follows:
Unpredictable LLMs are grabbing unstructured conversations, leaving us in the dark about what's happening.
Sometimes, the answers we get are not authentic, missing the mark on accuracy and relevance.
We're not keeping a tight enough grip on who owns what, especially regarding intellectual property and copyright.
With so much social engineering happening, we face a real risk of fraud and cybersecurity problems.
Even though this groundbreaking technology has some significant risks and hurdles, companies can safeguard their private information and build stronger customer relationships through careful management and powerful tools.
Conversational AI vs. Generative AI
Conversational AI and generative AI have distinct ultimate objectives. Conversational AI aims to comprehend human speech and the natural flow of conversation. It can be tailored to provide suitable responses to various queries and avoid addressing questions outside its scope.
On the other hand, generative AI strives to produce fresh, original content by drawing insights from existing customer data. It's inclined to answer out-of-scope questions with novel and imaginative responses. However, the quality of its answers might not align with your expectations, and it may not grasp the customer's underlying intent as effectively as conversational AI.
Having said this, it's worth emphasizing that many AI tools integrate both conversational AI and generative AI technologies. These systems utilize conversational AI to process user input and then leverage generative AI to formulate responses. This integrated approach effectively addresses challenges associated with use cases that extend beyond the capabilities of conversational AI alone.
Let's look at a quick comparison of Conversational AI vs. Generative AI in a tabular manner:
Aspect | Generative AI | Conversational AI |
|---|---|---|
Primary Function | Creates new content, ideas, or designs. | Enables natural language interactions and responses. |
Use Cases | Content generation, design, and coding. | Chatbots, virtual assistants, and customer support. |
Output Type | Produces diverse creative content. | Primarily generates text-based or voice-based responses. |
Creativity Level | High—focuses on originality and novelty. | Varies—ranging from structured to dynamic interactions. |
Applications | Art, design, content creation, and innovation. | Customer service, virtual assistants, and personalized marketing. |
Interaction Type | Typically one-sided (e.g., generating text or images). | Engages in two-way communication, responding to user inputs. |
Learning Approach | Trained on extensive datasets to recognize patterns for creative output. | Uses conversational datasets to interpret and respond to user queries. |
Examples | AI-generated artwork, language translation, and creative writing. | AI chatbots like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. |
Wrap Up
Both technologies provide unique advantages and capabilities across different scenarios. GenAI fosters creativity and scalability, while conversational AI helps users become more comfortable with the ecosystem. When used together, these technologies benefits and potential applications grow significantly for businesses, teams, and end users.
Enter Waves and Atom by Smallest.ai.
Trusted by 400+ companies like People+ai, Vocode, and BOLNA, Smallest.ai has entwined both the technologies to enhance real-time AI agents and Human-like voice experiences. Smallest.ai is at the forefront of delivering real-time artificial intelligence solutions that emphasize hyper-personalization, low latency, and scalability. Their innovative platforms are designed to transform AI-human interactions efficiently and affordably, catering to a diverse range of applications across various industries.
Are you curious to learn more about Smallest.ai? Take it for a free spin today!
FAQs
1. What is Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)?
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is a technology that converts spoken language into written text. It uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to analyze speech patterns, recognize words, and transcribe audio in real-time or post-processing. ASR is widely used in voice assistants, transcription services, customer support automation, and accessibility tools, enabling seamless human-computer interaction through voice commands.
2. What is the difference between a chatbot and conversational AI?
Conversational AI includes a broad spectrum of tools and systems that allow computer software to communicate with users. AI-powered chatbots are one of the software that uses conversational AI to interact with people.
3. What is the future of conversational AI?
Conversational AI is the technology that enables natural and human-like interactions between humans and machines using voice or text. The increasing demand for conversational commerce will drive the future of conversational AI, the expanding reach of languages and form factors, the improving technology, and new venues like the metaverse. The conversational AI market is expected to grow to $15.7 billion globally by 2025.
4. How has conversational AI revolutionized customer support automation?
Conversational AI has completely transformed customer support automation by leveraging natural language processing and deep learning techniques. Automatic speech recognition, NLP algorithms, and machine learning enable seamless customer interactions and chatbots. This revolution has empowered businesses to provide personalized and efficient customer service.

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now


