Learn how AI in mobile banking drives real-time security, conversational service, and scalable execution across high-impact banking use cases. Read more.

Ranjith M S
Updated on
February 24, 2026 at 8:53 AM

When leaders search for AI in mobile banking, it is rarely an exploratory exercise. It usually follows an operational signal. Fraud review queues are expanding faster than risk teams can clear them. Mobile support volumes are rising while resolution times slip. Voice and chat channels are struggling to keep pace with real-time customer expectations inside the app.
That pressure explains why AI in mobile banking is projected to reach an estimated value of USD 10.85 billion by 2033. Banks and fintech operators are adopting AI to execute live interactions, secure in-session transactions, and maintain service continuity without linear cost growth.
In this guide, we break down where AI delivers measurable operational impact, how it changes mobile banking execution, and what the next phase looks like for enterprise teams.
Key Takeaways
Operational Pressure Is the Trigger: Banks adopt AI in mobile banking to respond to real-time fraud, rising support volumes, and service latency that legacy automation cannot handle at scale.
Real-Time Execution Defines Value: The highest-impact AI use cases operate during live sessions and transactions, stopping fraud, resolving issues, and guiding customers before failures escalate.
Conversational AI Drives Service Continuity: Voice- and text-based AI allows accurate, low-latency financial conversations that reduce contact center load while preserving compliance and numeric precision.
Security Shifts From Review to Intervention: AI-driven fraud prevention succeeds when it detects threats in-session, applies adaptive controls, and produces audit-ready enforcement decisions.
The Next Phase Is Infrastructure, Not Features: Future-ready mobile banking relies on always-on intelligence, agentic execution, and governed human–AI workflows embedded directly into banking operations.
Why Banks Require AI in Mobile Banking
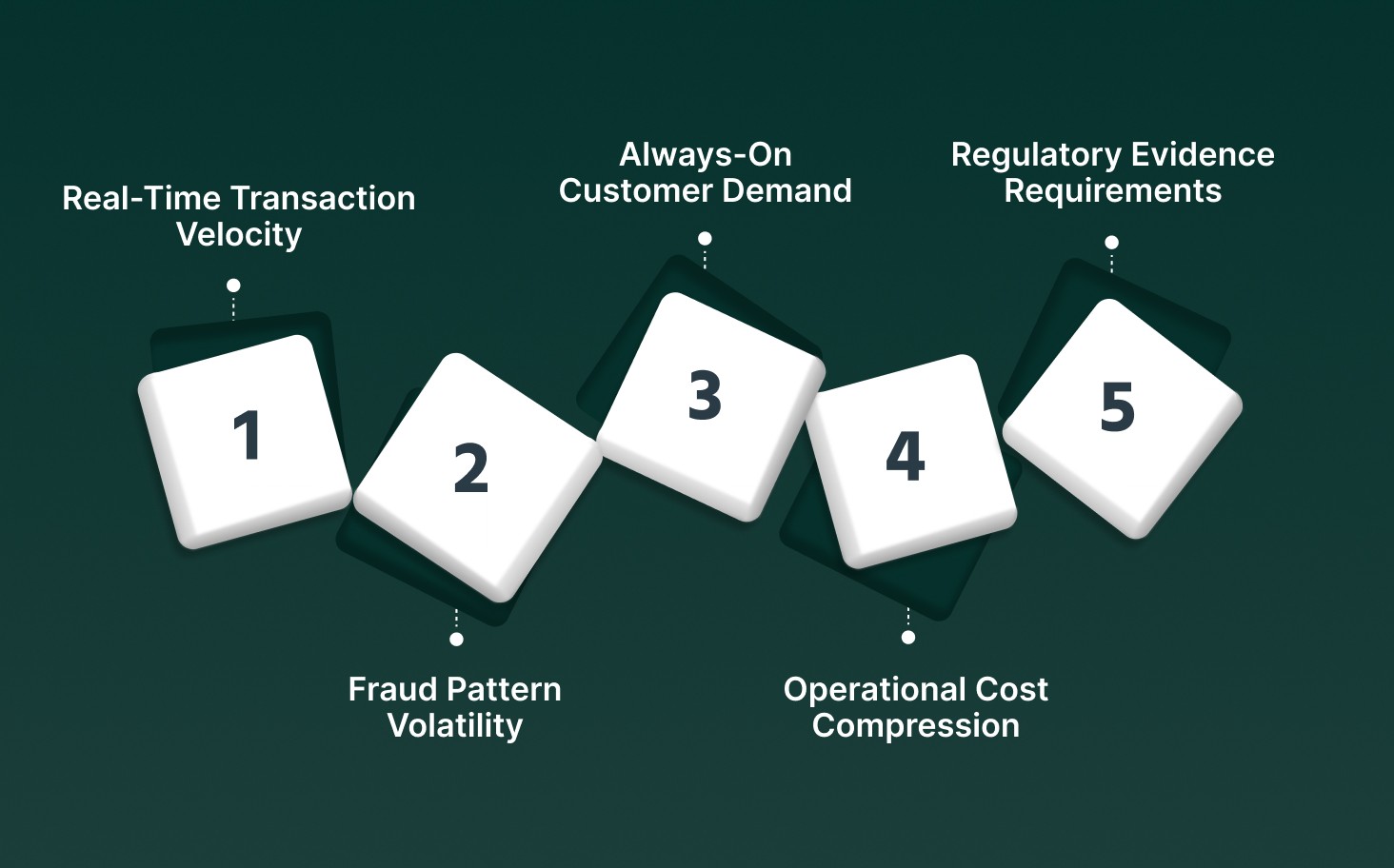
Banks adopt AI in mobile banking to manage real-time financial risk, sustain service continuity at scale, and execute customer interactions with precision that manual and rules-based systems fail to deliver.
Real-Time Transaction Velocity: Mobile banking transactions occur in milliseconds across UPI, cards, and instant payment rails, requiring AI models that score behavioral risk continuously during session execution, not after settlement.
Fraud Pattern Volatility: Fraud vectors shift faster than static rules can be updated, making machine learning models necessary to detect novel attack sequences, device spoofing, and social engineering patterns mid-flow.
Always-On Customer Demand: Mobile users expect immediate resolution for balance checks, disputes, and payment failures, which forces banks to deploy AI-driven service layers that operate without agent availability constraints.
Operational Cost Compression: High-volume, low-complexity interactions overwhelm contact centers, and AI allows automated handling with traceable decision logic that reduces cost per interaction without sacrificing control.
Regulatory Evidence Requirements: Supervisors require explainable decisions for fraud actions, credit assessments, and customer communications, which AI systems provide through logged inference paths and auditable execution trails.
AI is required in mobile banking because real-time financial systems demand continuous intelligence, verifiable decisions, and scalable execution that legacy automation cannot support.
See how automation drives measurable impact across core banking workflows in Top 16+ RPA Use Cases Transforming the Banking Industry
Core Use Cases of AI in Mobile Banking
AI in mobile banking is applied where real-time execution, conversational accuracy, and operational scale intersect. The most effective use cases focus on live decisioning, customer interaction automation, and operational control within mobile-first environments.
1. Transaction Intelligence and Behavioral Risk Analysis
AI models monitor live transaction flows and user behavior inside mobile sessions to detect risk signals and operational anomalies before financial impact occurs.
Session-Level Behavior Modeling: Tracks device fingerprints, navigation patterns, and interaction timing to identify abnormal behavior during active mobile sessions.
Real-Time Anomaly Scoring: Evaluates transactions against historical baselines within milliseconds, allowing intervention before payment completion.
Continuous Risk Recalibration: Updates risk scores dynamically as user behavior evolves within a single session, not across static checkpoints.
2. Conversational Service Automation for Mobile Users
AI-driven conversational systems handle high-frequency banking interactions through voice and text while maintaining accuracy in financial data and compliance-sensitive responses.
Multi-Turn Financial Dialogue Handling: Maintains conversational context across balance inquiries, transaction explanations, and follow-up questions without losing numeric accuracy.
Latency-Sensitive Voice Interactions: Responds within sub-second thresholds to support real-time voice conversations inside mobile banking workflows.
Controlled Escalation Logic: Transfers conversations to human agents only when confidence thresholds or compliance rules require intervention.
3. Automated Account and Payment Servicing
AI systems manage repetitive servicing workflows that traditionally require agent involvement, reducing resolution time and operational load.
Payment Status and Failure Resolution: Explains declined, pending, or reversed transactions using transaction metadata and real-time processing states.
Proactive Customer Outreach: Initiates voice or text interactions for overdue payments, upcoming debits, and account actions based on trigger conditions.
Structured Compliance Logging: Records every interaction, response, and decision path to support audit and dispute resolution processes.
4. Voice-Based Authentication and Verification
AI allows secure user verification during mobile interactions without relying on static credentials or disruptive security steps.
Passive Voice Biometrics: Authenticates users during natural speech without requiring explicit security prompts.
Risk-Adaptive Verification: Applies additional checks only when transaction or session risk exceeds defined thresholds.
Replay and Spoof Detection: Identifies synthetic or recorded voice attacks through acoustic and behavioral signal analysis.
5. Proactive Fraud Confirmation and Resolution
AI systems engage users in real time when suspicious activity is detected, reducing false positives and delayed account actions.
Instant Fraud Confirmation Calls: Initiates outbound voice interactions within seconds of anomaly detection.
Context-Aware Questioning: Confirms intent using transaction-specific prompts rather than generic security questions.
Immediate Action Execution: Freezes cards, blocks transactions, or restores access based on verified customer responses.
6. Mobile Lending Prequalification and Application Support
AI assists users through early-stage lending interactions directly within mobile channels, reducing friction and abandonment.
Real-Time Eligibility Assessment: Evaluates income signals, transaction behavior, and repayment capacity during app sessions.
Conversational Application Guidance: Explains documentation needs, timelines, and next steps through voice or chat.
Drop-Off Recovery Triggers: Re-engages users who abandon applications with context-aware follow-up interactions.
7. Credit and Repayment Engagement
AI manages borrower communications post-disbursement, balancing repayment outcomes with regulatory and customer experience requirements.
Personalized Repayment Conversations: Adjusts tone and cadence based on delinquency stage and borrower behavior.
Voice-Led Negotiation Flows: Supports structured repayment discussions without exposing agents to compliance risk.
Outcome-Based Interaction Tracking: Logs agreements, promises to pay, and customer responses for audit review.
8. Multilingual Customer Support at Scale
AI expands mobile banking reach by allowing accurate, real-time conversations across languages and regional dialects.
Real-Time Language Detection: Automatically identifies customer language preference during live interactions.
Consistent Financial Terminology Handling: Preserves numeric accuracy, currency references, and regulatory phrasing across languages.
Unified Service Logic: Applies identical workflows and controls regardless of language channel.
Core AI use cases in mobile banking succeed when systems operate in real time, handle financial conversations with precision, and execute securely at scale across voice and text channels.
See how autonomous systems are handling fraud alerts, investigations, and service workflows at scale in AI Agents in Banking: Automating Fraud Detection & Account Services
AI for Mobile Banking Security and Fraud Prevention

AI secures mobile banking environments by detecting, assessing, and responding to threats during live user sessions, where delays or misclassification directly translate into financial loss or customer distrust.
Session-Level Threat Detection: Monitors device behavior, interaction cadence, and navigation anomalies throughout an active mobile session rather than relying on post-transaction review.
Adaptive Risk Scoring: Continuously recalculates risk based on evolving user actions, transaction context, and historical behavior during the same session.
Real-Time Intervention Controls: Triggers step-up verification, transaction holds, or customer confirmation before authorization completes.
Synthetic and Social Engineering Defense: Identifies replay attacks, scripted interaction patterns, and manipulation signals common in mobile fraud scenarios.
Audit-Ready Decision Tracing: Captures model inputs, risk scores, and enforcement actions to support forensic analysis and regulatory review.
AI-driven security and fraud prevention protects mobile banking systems only when it operates in real time, intervenes decisively, and produces traceable enforcement decisions.
Explore how leading banks apply forecasting models across risk, revenue, and operations in 9 Types of Predictive Analytics in Banking Used by Top Teams
What the Next Phase of AI in Mobile Banking Looks Like
The next phase of AI in mobile banking shifts from feature-level automation to real-time execution infrastructure, where intelligence operates continuously across customer interactions, transactions, and operational controls.
Always-On Intelligence Layers: AI systems remain active across sessions, channels, and transaction states, allowing uninterrupted monitoring and response without user initiation.
Agentic Workflow Execution: Autonomous agents execute predefined banking actions such as verification, follow-ups, and service resolution within controlled policy boundaries.
Real-Time Voice as Primary Interface: Voice becomes a default interaction layer for time-sensitive banking actions, reducing dependency on app navigation and text input.
Embedded Compliance Controls: Regulatory rules, audit logic, and escalation thresholds are enforced directly within AI execution flows rather than post-event review.
Human-AI Operating Models: Clearly defined handoff points allow human teams to supervise exceptions while AI handles standard execution paths.
The future of AI in mobile banking is defined by continuous execution, governed autonomy, and real-time interfaces rather than isolated automation features.
How Smallest.ai Supports Real-Time Voice AI in Mobile Banking
Smallest.ai provides a full-stack voice AI foundation designed for real-time banking environments where latency, speech accuracy, and execution reliability determine customer trust and operational control.
Sub-100-ms Voice Latency: Generates natural speech in under 100 milliseconds, enabling uninterrupted, real-time conversations during live mobile banking interactions.
Human-Grade Speech Models: Uses in-house trained voice models built on millions of real conversations to preserve pacing, intonation, and numeric clarity in financial dialogue.
Agentic Voice Execution: Supports configurable voice agents that can execute instructions, reference knowledge bases, and follow deterministic flows for banking-grade use cases.
Enterprise Deployment Flexibility: Runs securely in cloud or on-premise environments, allowing banks to control data residency, inference ownership, and infrastructure constraints.
Compliance-Ready Architecture: Aligns with SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and PCI standards, with structured logging and audit support built into voice execution workflows.
Smallest.ai allows banks to treat voice AI as a real-time execution infrastructure rather than a surface-level interface, supporting secure, low-latency banking conversations at scale.
Conclusion
AI in mobile banking increasingly defines how well institutions execute under pressure. The difference is no longer visible in feature checklists or app interfaces. It shows up in how quickly risk is contained, how clearly customers are guided through critical moments, and how reliably systems perform when volumes spike without warning. Banks that treat AI as a real-time execution infrastructure gain operational control that static automation cannot provide.
If your teams are evaluating how to support live voice interactions, secure high-velocity transactions, and scale mobile service without adding friction, it may be time to assess purpose-built voice AI infrastructure.
Explore how Smallest.ai supports real-time, enterprise-grade conversational execution across mobile banking workflows. Get in touch with us!
Answer to all your questions
Have more questions? Contact our sales team to get the answer you’re looking for

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now


