See how the future of AI in customer service reshapes voice, text, and agent workflows with real use cases and clear steps teams can act on. Read more.

Prithvi Bharadwaj
Updated on
January 27, 2026 at 5:49 AM

Customer service leaders know the daily pattern too well, rising queues, uneven traffic, and agents pushed into repetitive tasks that drain time from calls that actually need human judgment. The pressure points are clear, and they are arriving faster than teams can absorb. This is where the future of AI in customer service shifts from prediction to operational necessity.
Budgets signal the same direction. The AI for customer service market expands from USD 12.10 billion in 2024 to USD 117.87 billion by 2034, driven by enterprise demand for real-time systems that can listen, respond, and act across channels. Voice AI, conversational AI, voice agents, and accurate voice cloning are becoming standard components in contact centers that manage high volume without sacrificing quality.
As this momentum continues, the future of AI in customer service centers on faster responses, stronger context, and workloads that move away from agents and into systems designed to handle them.
In this guide, you will see how these shifts affect day-to-day operations and what teams need to prepare for.
Key Takeaways
Rising Interaction Pressure: Interaction spikes across channels now exceed what frontline teams can manage without real-time automation to absorb concurrency.
End-to-End Agentic Execution: Future agentic systems complete multi-step billing, claims, onboarding, and policy workflows without switching tools or requiring handoffs.
Emotion-Aware Conversation Control: Voice and text models adjust tone, pacing, and escalation by tracking vocal stress, rhythm changes, and intent shifts during the interaction.
Self-Service That Updates Itself: Knowledge flows develop automatically as AI rewrites steps and reorganizes guidance based on real usage patterns and emerging issues.
Latency as the Automation Gatekeeper: Sub-second responses and dependable system access drive higher containment, cleaner handoffs, and reduced repetitive workload for human agents.
What Customer Service Teams are Dealing With Right Now
Service leaders are seeing customer behavior shift faster than current workflows can handle. The challenge is not volume alone but fast requests, constant channel switching, and interactions that change midstream. Each shift forces agents to rebuild context.
This is why the future of AI in customer service is now part of daily planning. Leaders want clarity on which tasks AI can absorb, which moments need humans, and how this balance will reshape frontline roles
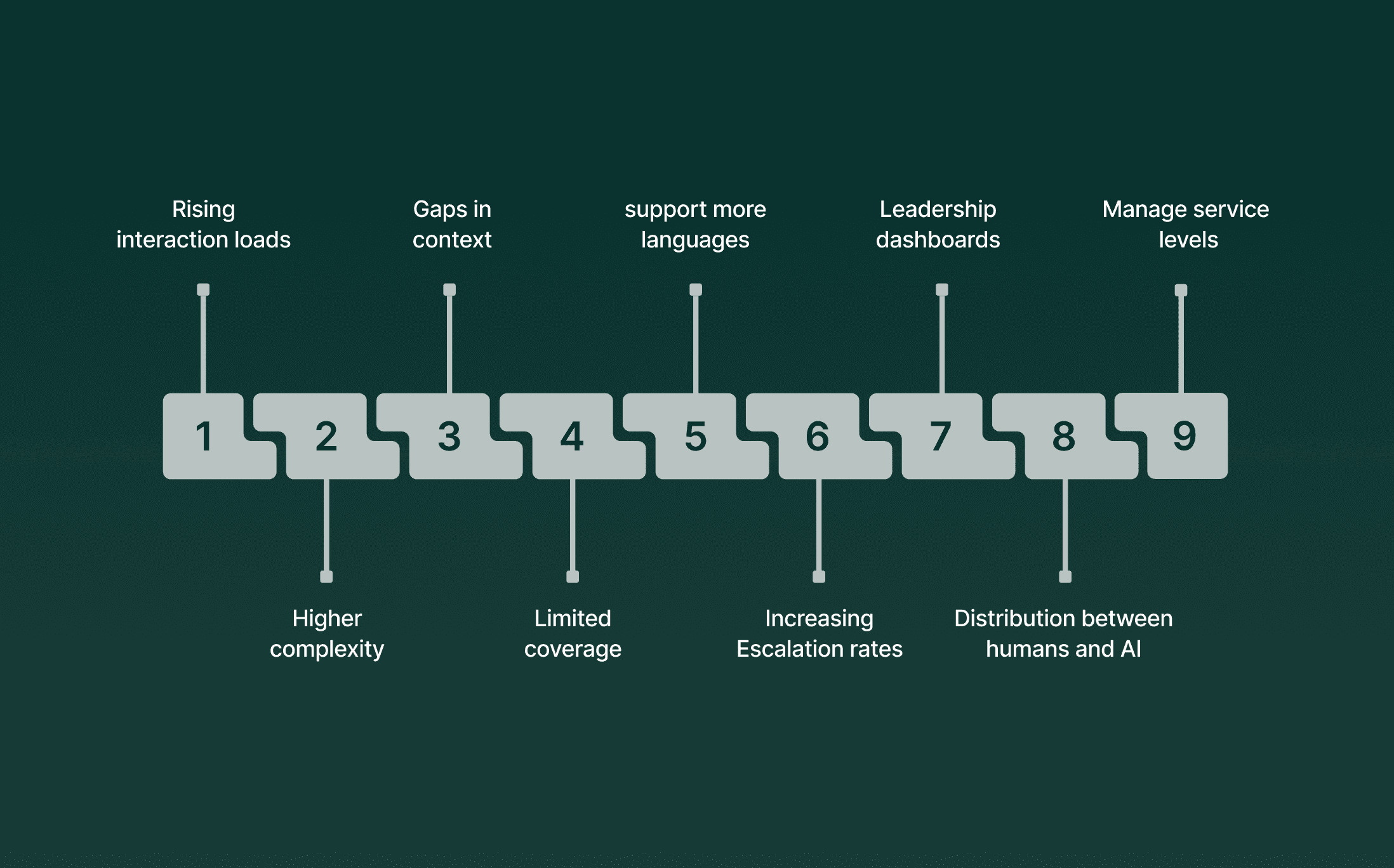
Rising interaction loads across voice and messaging: More customers contact support across multiple channels within the same issue cycle, creating concurrency levels that frontline teams cannot absorb.
Higher complexity in routine conversations: Even simple calls now include verification steps, policy checks, and backend lookups that add friction for agents already switching between tools.
Gaps in context during cross-channel transitions: When a customer moves from self-service to a live agent, most centers lose the full thread, forcing repeated questions and slowing outcomes.
Limited coverage for late-night and weekend traffic: Teams struggle to maintain response standards outside daytime hours, which leads many leaders to explore when and where AI can step in.
Growing pressure to support more languages: U.S. enterprises expanding nationwide receive requests in wider language mixes, creating staffing strain for roles that require bilingual skills.
Escalation rates are increasing during peak cycles: Agents push more cases upward because they cannot access the data, steps, or guidance needed for first-touch resolution.
Workforce strain reaching leadership dashboards: Supervisors spend a growing share of time coaching agents through avoidable delays rather than improving long-term operations.
Uncertainty around role distribution between humans and AI: Leaders reviewing AI will replace customer support, or can AI replace customer service? Want clarity on which tasks AI can carry out with precision and which tasks still need human oversight.
Pressure to manage service levels without expanding teams: Budgets remain flat while expectations rise, pushing leaders toward systems that can handle spikes and maintain consistency.
For a clearer view of how leading teams plan their next automation upgrades, read 10 Best Customer Service Automation Practices for 2025
Where AI is Heading and Why it Matters for Service Operations
Service operations are entering a phase where AI handles far more than recognition and response. The next wave focuses on full task execution, early detection of customer friction, and deeper awareness of caller behavior.
These systems coordinate actions across billing, claims, devices, and policy data while adjusting course in real time when conditions change. The shift matters because it reshapes how teams distribute work, manage volume, and maintain service quality during complex interactions.
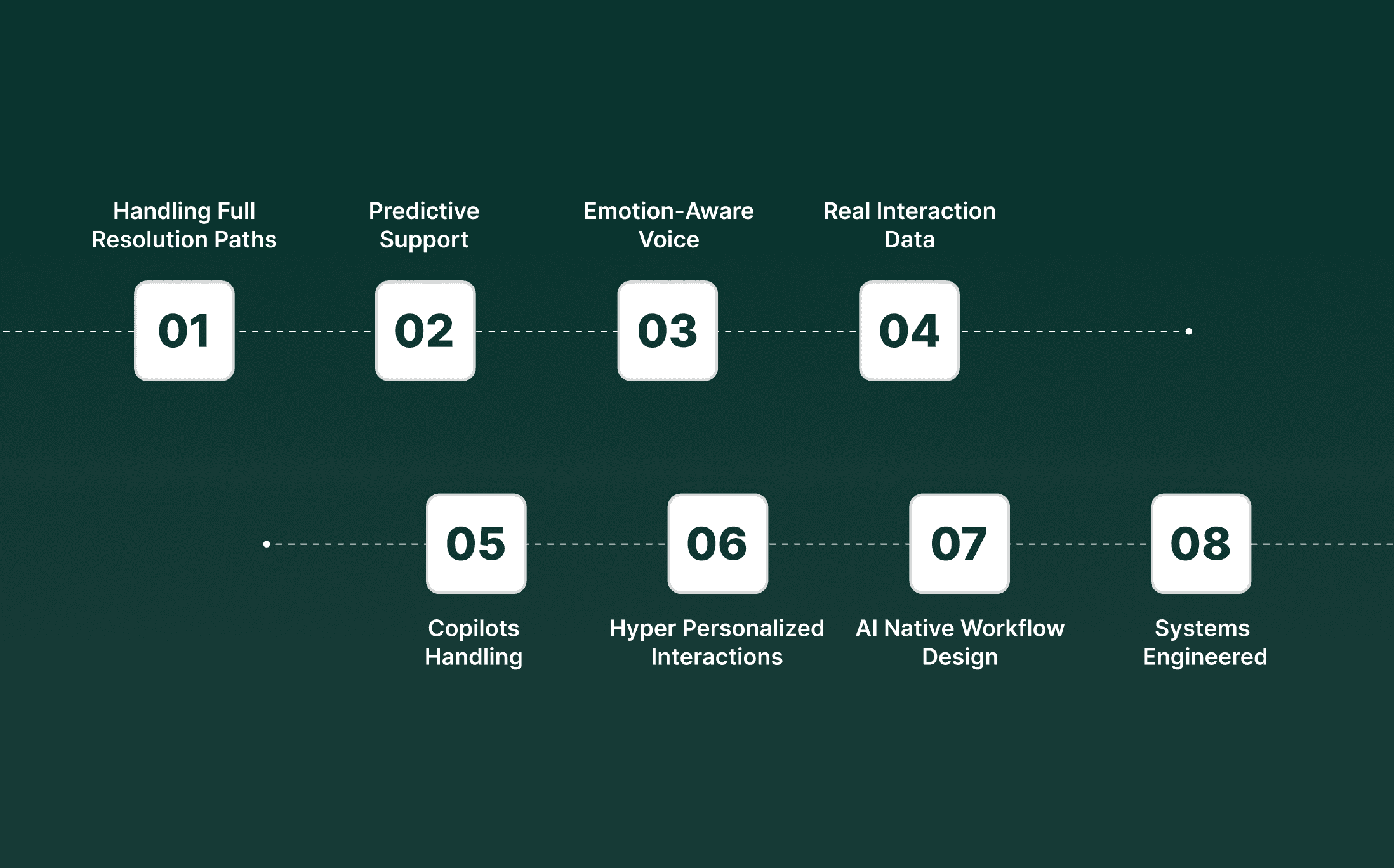
1. Agentic Systems Handling Full Resolution Paths
Future AI won’t stop at answering questions. It will execute multi-step service tasks across billing, claims, appointments, onboarding, and policy actions without bouncing between tools.
Multi-step execution without handoffs: A future agent handling a billing dispute will pull transaction history, check plan rules, confirm eligibility, adjust the charge, and send a confirmation, without passing through five tools.
System reasoning across business apps: The agent evaluates inputs from CRM, ticketing, knowledge, and policy systems, then sequences actions based on the most direct path to resolution.
Real-time course correction during execution: If the customer changes their request mid-interaction, the workflow shifts instantly rather than forcing a restart.
2. Predictive Support That Acts Before Customers Reach Out
Service moves from reactive recovery to early detection. Future systems quietly monitor behavior patterns, device signals, account actions, and system data to intervene before issues create friction.
Early detection of rising friction: Future models scan behavior patterns, repeated login failures, delivery delays, policy mismatches, and trigger outreach before customers escalate.
Automated fixes in the background: A device configuration issue could be resolved silently by the system, with a message sent afterward explaining what changed.
Contact surge forecasting for operations: AI notices early spikes in error codes or product failures and alerts workforce teams so they can rebalance capacity days before volume peaks.
3. Emotion-Aware Voice And Text Models Guiding Interaction Choices
Next-generation models read far more than keywords. They track vocal pace, stress cues, conversation rhythm, and intent shifts to shape how the system responds in sensitive moments.
Real-time sensitivity shifts: If a caller’s voice tightens or rhythm changes, the system slows its pace, simplifies explanations, or moves closer to human escalation.
Support for high-stakes conversations: In sectors like healthcare or financial services, models identify nervousness or confusion and surface compliance-safe phrasing for sensitive steps.
Safe handoff when emotional strain escalates: The AI recognizes when continuing automation risks frustration and transfers to a human with full context captured.
4. Self-Service That Grows Automatically From Real Interaction Data
Self-service will stop functioning as a static library. It becomes a living system that updates based on live usage patterns.
Content rewritten from emerging issues: If hundreds of customers attempt a step that repeatedly fails, the AI rewrites that answer to reflect the correct sequence, without waiting for a service team to update it.
Guided flows built from real patterns: Common troubleshooting paths adapt weekly based on fresh query clusters, removing outdated logic and unnecessary steps.
Navigation shaped by customer behavior: Future systems track where users pause or backtrack, then rearrange steps to reduce cognitive load.
Experience voice systems that return natural audio in milliseconds and complete tasks across your internal tools. Book a demo with Smallest.ai.
5. Agent Copilots Handling Cognitive Load During Calls
AI copilots grow from shortcut tools to full session companions for agents.
Instant retrieval of everything that matters: During a call, the copilot surfaces past tickets, payments, device data, and policy details without the agent searching.
Next step reasoning for complex scenarios: If an agent helps a caller reset a locked account with multiple dependencies, the copilot maps out the exact required sequence and prompts each step.
Automatic completion of post-call tasks: Draft summaries, outbound messages, order updates, and internal notes are produced instantly, freeing agents from repetitive admin work.
6. Hyper Personalized Interactions Shaped By Live Behavior
Personalization moves from stored preferences to moment-based interpretation.
Behavior-driven adjustments: If a caller sounds uncertain, the AI shifts to clearer phrasing; if confident, it shortens guidance.
Routing shaped by real-time context: A claim caller showing early signs of confusion goes directly to a human instead of being kept in automation.
Offers based on active intent: Recommendations appear only when the caller’s actions indicate readiness, not when a static profile suggests it.
7. AI Native Workflow Design Replacing Legacy Service Architecture
The meaningful change is structural; organizations redesign service flows so AI handles mechanical workload while humans stay focused on judgment.
Processes arranged to reduce human repetition: Identity checks, multi-system lookups, status requests, and order adjustments move entirely to automation.
Clear division between automation and human contribution: Humans handle disputes, exceptions, emotional cases, and regulatory gray areas.
Unified oversight for trust and auditability: All AI actions, decisions, and escalations are logged in a traceable record, supporting internal and regulatory review.
8. Systems engineered for operational KPIs, not feature demos
Enterprises adopt AI to impact workload distribution, staffing strategy, accuracy, and compliance, not to add conversational features.
Predictable handling time ranges: AI follows deterministic steps that reduce variability in interaction length, which supports planning and staffing models.
Actionable data from every interaction: Every call produces structured outputs: reason codes, task-level timestamps, routing triggers, and summary fields.
Research-backed adoption trends: A recent survey found 85% of customer service leaders plan to explore or pilot customer-facing conversational generative AI in 2025.
Taken together, these developments point to an operational future shaped by systems that act, adapt, and support teams through full resolution cycles.
What Current Deployments Reveal Through Real Benchmarks
Recent deployments show how AI behaves under real traffic, real policies, and real operational pressure. Leaders reviewing these benchmarks focus on where systems deliver consistent workload support and where human judgment remains essential.
These insights also shape how teams plan the balance between automation and human roles in high-volume service environments.
Automation coverage tied to latency and handoff quality: Centers with sub-second responses recorded higher containment, while sites with slower turn-taking saw repeated interruptions that reduced coverage.
Complex case handling limited by data access: AI resolved multi-step requests only when connected to accurate records, policy data, and clear rule paths.
Peak-hour traffic reveals model resilience: Night and weekend spikes exposed whether models could maintain stable pacing without response drift or rising error rates.
Multilingual flows perform better with automatic detection: Deployments using early language detection avoided transfers and produced shorter interactions during mixed-language sessions.
Agent workloads drop when AI manages routine checks: Teams reported fewer repetitive tasks when AI completed identity steps, pulled account data, or handled basic policy queries.
Escalation quality is higher with structured summaries: Supervisors received cleaner context when AI passed cases upward using concise, time-stamped summaries drawn from the live session.
Training loops improve with structured outputs: Centers using AI-generated reason codes and timestamps refined routing rules faster than teams relying on manual notes.
For teams improving call quality without adding agent load, review Key Benefits of Voice AI in Customer Service
What Enterprises Need Before Bringing Voice and Text AI to Scale
Enterprises aiming to scale voice and text automation need a foundation that keeps timing steady, data reliable, and workflows controlled. The focus shifts from model accuracy alone to whether the system can operate inside real policies, connect with internal tools, and maintain traceable actions across every call and chat interaction.
Low-Latency Delivery Across All Calls: Voice AI must respond within human turn-taking limits to prevent interruptions, repeats, and rising abandonment.
Stable Access to Internal Systems: AI needs reliable access to CRMs, case systems, billing layers, and verification checks to complete multi-step tasks without delays.
Strict Rule Paths for Regulated Interactions: Enterprises require clear workflows that keep every AI action inside approved compliance boundaries, with no deviation.
Unified Context Across Voice and Chat: Systems must retain interaction history, prior attempts, and caller details across channels so customers do not repeat information.
Time-Stamped Logs for Oversight and Audits: Every AI step should generate structured records that supervisors can review quickly during escalations or compliance checks.
These foundations help leaders deploy AI with confidence, protect service quality, and define where automation fits within existing teams and workflows.
Practical Steps to Introduce High-Impact AI in Contact Centres
Enterprises add AI to contact centres by proving reliability in small, controlled slices of real work before expanding coverage. The goal is to introduce automation without creating new friction for callers or agents while building confidence that the system can support a meaningful workload under daily pressure.
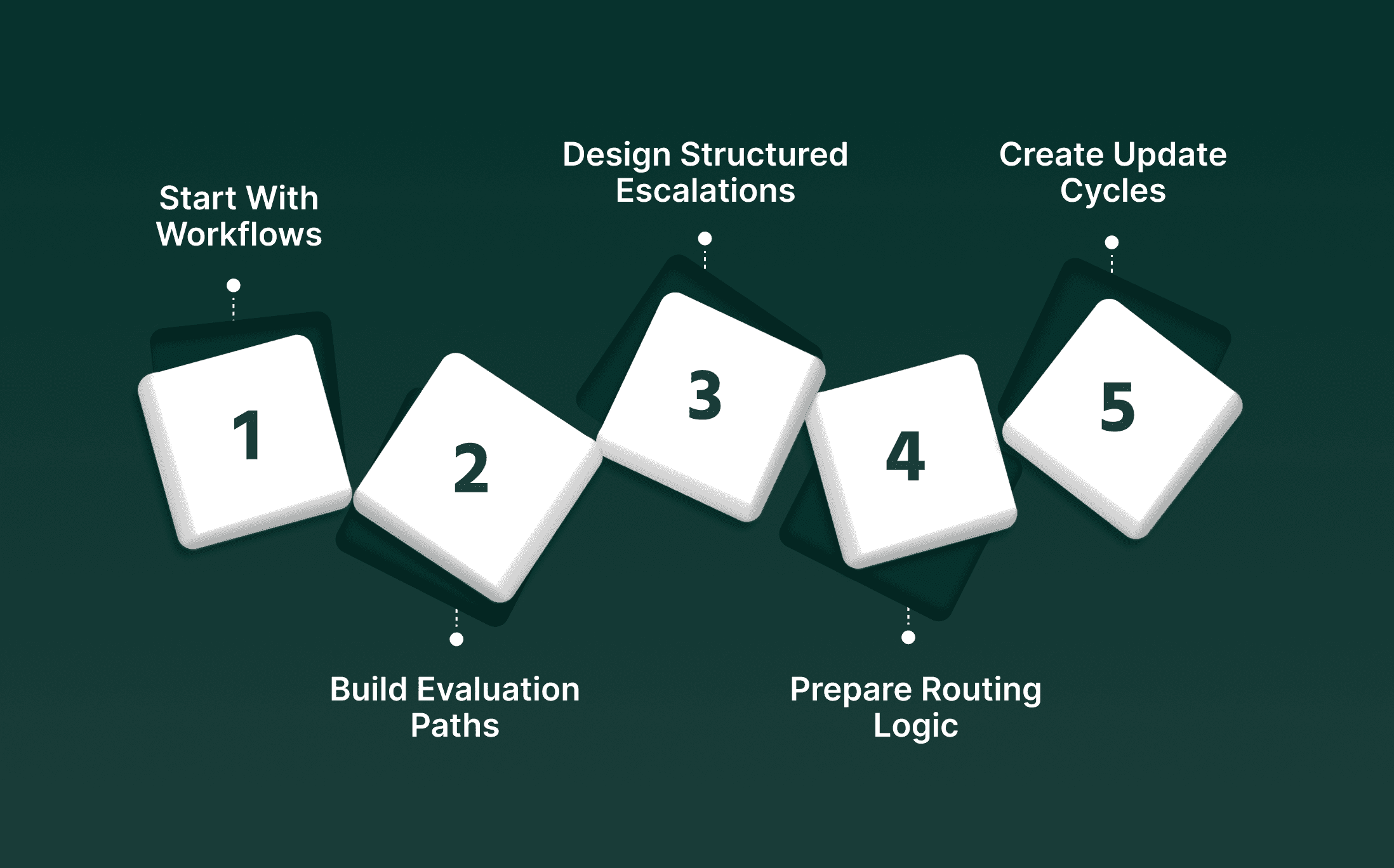
Start With Workflows That Follow Predictable Logic: Choose high-volume tasks with clear steps, stable data fields, and minimal judgment requirements.
Build Evaluation Paths for Accuracy and Latency: Track response speed, containment, and error patterns separately to understand where the model performs well and where risk appears.
Design Structured Escalation Channels: Create direct handoff rules so agents receive clean summaries, timestamps, and context when AI forwards a case.
Prepare Routing Logic for Mixed Traffic: Use complexity markers to decide when AI handles a request fully, shares the task, or sends it directly to a human agent.
Create Update Cycles for Prompts and Rules: Review scripts, rulesets, and model outputs on a fixed cadence so improvements do not destabilize live operations.
These steps help leaders introduce AI without disrupting service quality or compliance, while giving teams clarity on where AI can handle meaningful workload and where human agents remain essential.
How Smallest.AI Strengthens Voice and Agent Workflows for Customer Service
Enterprises need voice systems that stay steady under real call pressure while completing tasks within their existing tools. Smallest.ai supports this by pairing fast audio models with agents that act on live information, capture structured details, and move workflows forward without slowing callers or teams.
Real-Time Responses at Conversation Speed: Lightning Voice AI delivers natural responses with extremely low latency, supporting smooth turn-taking during calls.
Full-Stack Agent Actions Across Tools: Agents connect with CRMs, email, ticketing tools, and messaging apps to complete updates, send information, and trigger workflows.
In-House Models Trained on Millions of Conversations: Electron SLMs interpret caller intent, policy steps, and conversation cues with precision across complex use cases.
Voice Agents Built for 100+ Enterprise Workflows: Agents handle tasks such as customer support, debt follow-ups, screening, scheduling, and order updates with minimal human fallback.
Reliable Security Across Cloud and On-Premise: SOC 2 Type 2, HIPAA, PCI, and ISO-aligned controls support deployments in finance, health, logistics, and other regulated sectors.
Human-Like Voices in 16 Languages: Natural-sounding voices maintain clarity across accents and regions, supporting wide customer bases without additional staffing.
Structured Analytics and Call Intelligence: Real-time transcription and behavior analysis help supervisors track caller needs, internal bottlenecks, and resolution paths.
Quick Integration With Enterprise Systems: Connections to email, ticketing, CRM platforms, and telephony systems allow AI agents to take action without manual steps.
These capabilities help enterprises introduce AI into customer-facing operations with confidence, maintain service quality during peaks, and unlock the next phase of scalable voice-driven support.
Conclusion
Many leaders see change coming, but the real shift is how fast service operations are moving toward systems that can listen, speak, and act without slowing the customer down. The future of AI in customer service is no longer a distant milestone. It is shaping how teams plan capacity, distribute workload, and protect agent focus in environments that run on real-time accuracy. As expectations rise, the organizations that benefit most will be the ones that adopt tools built for live interaction rather than static automation. This is where the future of AI in customer service becomes a practical path, not a prediction.
That direction is already reflected in how modern platforms support voice-heavy operations. Smallest.ai brings voice AI, conversational AI, voice agents, and voice cloning into a single system designed for fast responses, stable performance, and clear handoffs that reduce strain on human teams.
Ready to see it in action? Book a demo.
FAQs About the Future of AI in Customer Service
1. How will AI affect customer service in voice-heavy industries?
AI helps with identity checks, account lookups, and routine steps so human teams can stay focused on calls that need judgment or verification.
2. Will AI replace customer support for late-night or high-volume traffic?
AI can cover after-hours spikes and overflow queues, but complex cases still need human review, especially when policies or sensitive details are involved.
3. How AI is changing customer service for teams with mixed languages?
Models detect language early in a call and switch without menus, helping centers serve multilingual regions without extra staffing.
4. Can AI replace customer service for common requests without hurting quality?
Yes for high-volume tasks with clear rules. No for disputes, financial concerns, or conversations where emotion or trust shapes the outcome.
5. What does the future of AI in customer service mean for supervisor roles?
Supervisors receive cleaner summaries, better case context, and real-time call signals, giving them more time for coaching and fewer manual checks.

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now


