Learn how voice AI is transforming business communication — from customer calls to internal workflows — with use cases, tools & practical guidance.

Akshat Mandloi
Updated on
December 26, 2025 at 11:27 AM

In recent years, voice’s role in business communication has moved from novelty to strategic asset. For example, in 2024, over 8.4 billion digital voice assistants were in use globally—more than the world population—highlighting how quickly voice has become pervasive in our daily lives and business interactions.
For companies, that means opportunity: voice AI now enables real-time, natural conversations between customers, employees, and systems—without waiting, typing, or switching channels. Whether it’s an AI agent answering customer queries, a voice assistant scheduling a meeting, or a proactive alert via call, voice AI is reshaping how organizations communicate internally and externally.
In this article, we explore what business communication with voice AI truly entails: the technologies involved, use cases across external and internal domains, how to pick the right platform, challenges to watch, and a roadmap to rollout at scale.
Key Takeaways
Voice AI brings real conversations to business communication—beyond scripted IVRs to natural, context-aware dialogue.
Start with high-volume, low-complexity use cases, then scale gradually using data-driven pilots.
Integration is non-negotiable—voice systems must connect with CRM, UC, and backend platforms.
Track metrics like latency, containment rates, customer satisfaction, and cost per interaction.
Prepare for evolving trends: real-time translation, proactive voice agents, and seamless voice + chat experiences.
What Does Voice AI Mean for Business Communication?
Voice AI refers to systems powered by artificial intelligence that let users interact via spoken language. Unlike traditional IVR or press-1 menus, modern voice AI understands natural speech, context, and intent—creating conversational experiences that feel more human and less robotic.
Distinction: Voice AI vs Text AI / Chatbots
While chatbots and text-based assistants are valuable, they operate via typing or selecting options. Voice AI brings an entirely different experience: hands-free, faster, and more intuitive. It unlocks scenarios where speaking is easier than typing—like driving, walking, or visually impaired users.
Where Voice AI Fits in Business Communication
Voice AI can be embedded in multiple communication layers:
External channels: customer support, sales calls, outbound calls, reminders.
Internal channels: voice assistants for staff, alerts, and system notifications.
Conversational fabric: voice AI can be part of omnichannel flows, handing off to chat or human agents as needed.
As companies adopt unified communication systems (UCaaS), integrating voice AI becomes a natural evolution—adding a voice-first interface on top of existing chat, email, and phone infrastructure.
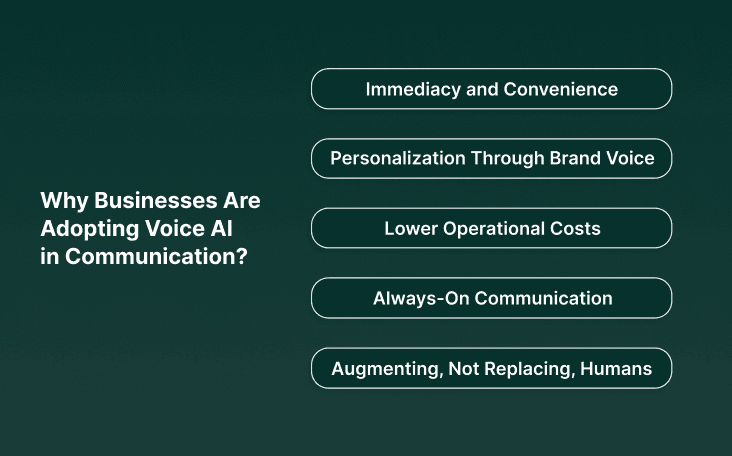
Why Businesses Are Adopting Voice AI in Communication
Businesses are under pressure to deliver faster, more personalized communication while keeping costs under control. Voice AI offers a practical way to bridge this gap. According to a Juniper Research report, voice assistants are expected to handle $164 billion worth of transactions annually by 2025, underscoring how central voice has become to both consumer and enterprise interactions
Here are the main drivers behind adoption:
1. Immediacy and Convenience
Typing on a screen takes effort. Speaking is natural and immediate. By letting customers and employees interact through voice, businesses reduce friction and speed up routine communication.
2. Personalization Through Brand Voice
Voice AI can be trained to match a company’s brand tone — warm and conversational for hospitality, concise and authoritative for finance. This builds consistency across thousands of daily interactions.
Companies exploring multilingual voice agents can extend personalization across markets — Top 10 AI Voice Agents with Multilingual Capabilities 2025.
3. Lower Operational Costs
AI-driven voice systems handle high-volume, low-complexity interactions — order updates, balance inquiries, appointment reminders — without consuming agent time. This reduces cost per interaction while freeing human staff for complex tasks.
4. Always-On Communication
Unlike human teams limited by shifts, AI voice agents provide 24/7 availability. This ensures global businesses can serve customers across time zones and respond instantly to after-hours inquiries.
5. Augmenting, Not Replacing, Humans
A common misconception is that voice AI eliminates jobs. In practice, it augments human agents: AI takes care of repetitive workflows, while employees focus on empathy-driven problem solving.
For a deeper look at how AI voice supports customer service automation, see How Voice AI Automation Can Speed Up Resolution Times.
Core Components Behind Voice AI for Business Use

Behind every natural-sounding AI conversation lies a stack of technologies working in real time. Understanding these layers helps businesses evaluate solutions and set realistic expectations.
Layer | What It Does | Why It Matters for Business Communication |
|---|---|---|
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) | Converts spoken language into text. | Accuracy with accents, dialects, and noisy environments ensures customer queries are captured correctly. |
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) | Interprets text to identify intent and context. | Enables systems to distinguish between “check my balance” vs. “open a balance account.” |
Dialogue Management | Controls the flow of conversation and escalation rules. | Keeps interactions smooth, handles clarifications, and ensures proper handoff to humans when needed. |
Text-to-Speech (TTS) / Voice Synthesis | Generates natural speech output in a chosen voice. | Delivers consistent brand tone across thousands of calls, in multiple languages. |
Integration Layer (CRM, UCaaS, ERP) | Connects the voice AI with customer data and communication tools. | Provides context so an AI agent knows the caller’s history before responding. |
Security & Compliance Frameworks | Encryption, role-based access, consent capture. | Critical for industries handling sensitive data (finance, healthcare, insurance). |
1. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) & NLU
ASR systems like Whisper or enterprise-grade speech models turn raw voice into structured text. NLU then makes sense of that text. Together, they allow business communication with voice AI to move beyond keyword spotting into real conversational understanding.
2. Dialogue Management
This is where voice AI moves from one-off commands to meaningful conversations. Dialogue managers track context (“Is this the same order number as before?”) and escalation rules to ensure smooth handovers.
3. Text-to-Speech (TTS) & Brand Voice
Modern TTS models generate lifelike speech that can be tailored to a company’s identity. For example, an e-commerce brand may choose a friendly tone, while a bank may prefer a clear, authoritative voice.
Companies can also explore pre-trained multilingual models to scale voice AI globally — Pre-trained Multilingual Voice Agent Models and Features.
4. Integration with Business Systems
For voice AI to be useful, it must connect with CRMs, ERPs, and contact center platforms. Without integration, agents lose context and workflows break. With it, a customer who says “check my last invoice” triggers an automatic CRM lookup.
Learn more about linking voice systems with CRMs here — Integrating Voice AI with CRM for Enhanced Efficiency.
5. Security and Compliance
Since calls often include sensitive data, solutions must comply with frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS. Encryption, consent recording, and audit logs are non-negotiables for enterprise adoption.
Voice AI in Action: External Use Cases
When most people think about business communication with voice AI, they picture customer-facing applications. This is where voice automation delivers the most immediate impact: higher availability, faster service, and reduced agent load.
1. Customer Support and Service Calls
Voice AI agents can handle tier-one inquiries such as password resets, billing questions, or order status checks. Instead of waiting in long queues, customers get instant answers — and live agents only step in for complex cases.
For practical insights into customer service automation, see How Voice AI Automation Can Speed Up Resolution Times.
2. Outbound Notifications and Reminders
Companies often spend heavily on manual outbound calls. With automation, reminders and alerts can be delivered at scale:
Appointment confirmations and rescheduling.
Payment due or renewal reminders.
Shipment or delivery notifications.
This reduces inbound call spikes while improving transparency.
3. Sales Calls and Lead Qualification
Voice AI can pre-qualify leads by asking scripted but conversational questions (budget, requirements, timeline) before handing them off to human reps. In outbound campaigns, this ensures sales teams focus on the highest-potential prospects.
4. After-Hours and Global Coverage
Customers don’t stop needing support at 5 PM. Automated call center services provide 24/7 coverage, answering queries across time zones without requiring night shifts.
5. Multilingual Customer Interactions
For global businesses, language barriers are a real challenge. Voice AI can instantly switch between languages or dialects, offering a seamless experience for diverse customer bases.
Explore top options for multilingual AI voice agents here — Top 10 AI Voice Agents with Multilingual Capabilities 2025.
Voice AI in Action: Internal Business Use Cases
Voice AI isn’t just for customers. Many companies are embedding it into internal workflows to make day-to-day operations faster and more intuitive. Here are some of the most practical applications:
1. Voice Assistants for Employees
Instead of clicking through menus, employees can use voice commands to:
Schedule meetings.
Check calendar availability.
Pull up client information during a call.
This improves productivity, especially in fast-paced roles like sales or customer service.
2. Automated Notifications and Alerts
Internal communication often relies on email or chat, which can be missed. Voice AI systems can deliver time-sensitive alerts through calls or voice announcements:
IT downtime notifications.
Compliance policy reminders.
Critical logistics updates.
In sectors like logistics, voice notifications keep drivers and warehouse staff informed in real time without manual calls.
3. Voice-Driven Dashboards and Reporting
Executives and managers can query dashboards hands-free: “Show me sales by region last quarter” or “What’s today’s average call volume?” Voice interfaces reduce friction in accessing data, especially on the go.
4. Voice Interfaces for Business Systems
Enterprises are experimenting with voice-first interactions for complex software: CRM, ERP, or HR platforms. Instead of navigating tabs, staff can say, “Update lead status to qualified” or “Add vacation leave for employee ID 245.”
Industry Examples
Healthcare: Doctors can use voice AI to retrieve patient records without typing during consultations.
Finance: Automated voice alerts for suspicious transactions improve fraud prevention.
Retail: Store managers can request real-time inventory updates via voice.
For deeper insight into how enterprises deploy voice AI stacks, see The Enterprise Voice AI Stack: A Complete Guide to Choosing the Right Solution in 2025.
Challenges and Risks in Business Voice AI Communication
While voice AI unlocks new possibilities, adopting it without foresight can backfire. Businesses should anticipate the main risks and put safeguards in place.
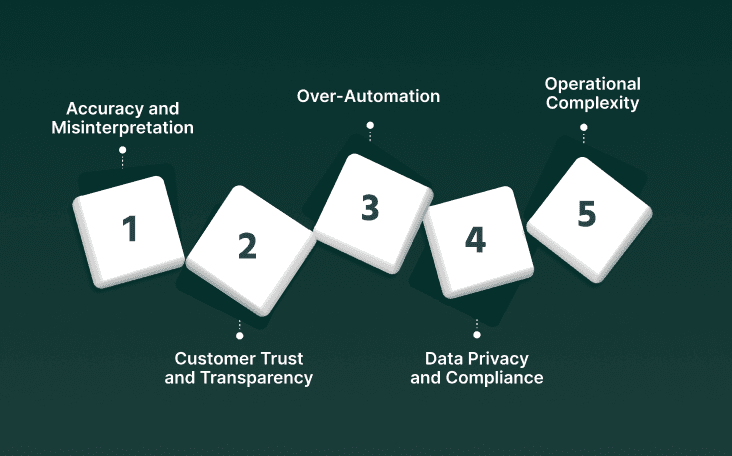
1. Accuracy and Misinterpretation
Even the best speech recognition can struggle with background noise, heavy accents, or domain-specific terms. Misunderstood queries frustrate customers and erode trust.
Solution: Train models with industry-specific data, and always provide a quick path to a human agent if the AI gets stuck.
2. Customer Trust and Transparency
Some customers feel uncomfortable if they don’t realize they are speaking to an AI agent. Poor disclosure can damage brand credibility.
Solution: Be transparent. A simple line like, “You’re speaking with our AI assistant, but I can connect you to an agent anytime,” builds trust while managing expectations.
3. Over-Automation
Using voice AI for every interaction risks alienating customers, especially for sensitive issues like billing disputes or medical inquiries.
Solution: Use automation to augment, not replace humans. Route emotional or complex conversations to live staff with context preserved.
4. Data Privacy and Compliance
Voice AI systems process sensitive data: credit card details, patient records, personal identifiers. Mishandling it can lead to regulatory fines or reputational harm.
Solution: Choose platforms that meet GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS requirements, and deploy encryption plus consent capture for every interaction.
5. Operational Complexity
Integrating voice AI into existing UCaaS, CRM, and ERP systems can be challenging. Poorly planned rollouts may disrupt workflows instead of improving them.
Solution: Start with pilots, test integrations in staging environments, and invest in observability tools to track errors and latency.
By treating these challenges as design constraints, businesses can adopt voice AI in a way that boosts communication without compromising compliance or customer relationships.
The Future of Voice-Driven Business Communication
Voice AI is moving from early adoption to becoming a core part of the business communication stack. As the technology matures, three trends stand out:
1. Real-Time Translation and Multilingual Support
Enterprises are increasingly global, yet language remains a barrier. Next-generation voice AI models can translate in real time, allowing a customer in Tokyo to speak Japanese while an agent in Toronto hears English instantly. This creates frictionless communication across markets.
For a closer look at multilingual capabilities, see Top 10 AI Voice Agents with Multilingual Capabilities 2025.
2. Proactive Voice Agents
Instead of waiting for calls, future voice AI systems will initiate communication. Imagine an AI agent that notices a service outage and proactively calls affected customers with updates, or a sales assistant that follows up on a lead before the competition does.
3. Multimodal Communication
Voice won’t operate in isolation. Businesses are moving toward multimodal experiences where voice, chat, and even video interact seamlessly. A conversation may start with a voice AI, move to text for document sharing, and escalate to a human with full context intact.
4. Lower Latency, Higher Naturalness
Emerging foundation models optimized for speech are pushing latency toward near-human response times. The difference between a 500ms pause and a 100ms response can make or break whether a customer perceives the system as natural.
Looking ahead, businesses that invest early in voice AI will be better positioned to meet rising customer expectations for instant, personalized, and global communication. The key is choosing platforms that can scale with these trends while maintaining compliance and brand consistency.
This is where Smallest.ai is already innovating — delivering real-time voice AI agents with <100ms latency, multilingual support, and enterprise-ready integrations that align with the next wave of business communication.
Conclusion
Voice AI is reshaping how businesses communicate—internally and externally. From support lines to employee assistants, the shift toward voice-first interactions is underway. The real winners will be those who adopt thoughtfully: selecting responsive, integrated voice platforms, defining clear use cases, and measuring impact rigorously.
Smallest.ai is purpose-built for this evolution. With real-time voice agents, global language support, and enterprise-grade compliance, it empowers businesses to move from theory to scale.
Ready to experiment? Explore Smallest.ai voice AI solutions and see how you can embed conversational voice into your communication stack today.
FAQs on Business Communication with Voice AI
1. What is voice AI in business communication?
Voice AI enables conversational interaction through voice, using speech recognition, natural language understanding, and text-to-speech to simulate human-like communication.
2. How do businesses use voice AI externally?
Common use cases include customer support calls, automated outbound reminders, sales pre-qualification, and after-hours assistance.
3. Can voice AI be used internally within companies?
Yes—voice assistants can help employees schedule meetings, retrieve info, receive alerts, and query business dashboards hands-free.
4. What criteria should be used to choose a voice AI platform?
Key factors include latency, language support, integrations (CRM, UCaaS), customization, analytics, and compliance.
5. What are common risks when implementing voice AI?
Risks include misinterpretation, over-automation, data privacy issues, and degraded customer trust—mitigated by fallback paths, transparency, and robust governance.
6. What future trends are transforming voice-based business communication?
Expect real-time translation, proactive voice agents (that initiate calls), and seamless voice + chat transitions in omnichannel systems.

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now