Learn the fundamentals of Speech-to-Text AI, its key features, functionality, and how it converts speech into accurate text, enhancing real-time communication.

Wasim Madha
Updated on
February 24, 2026 at 8:57 AM

In a world where every second counts, businesses are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency. If you’re working in customer service or healthcare, you know the pain of relying on manual transcription or struggling with inaccurate voice recognition. The bottlenecks caused by these outdated methods can slow down workflows and frustrate customers and employees.
This is where Speech-to-Text AI steps in. A Stanford study even revealed that speech recognition is three times faster than typing on smartphones, with a 20.4% lower error rate.
In this blog, we’ll break down what Speech-to-Text AI really is, how it works, and the ways it’s transforming industries by accelerating real-time communication, reducing errors, and making your workflows smarter. Let’s jump in.
Quick Recap
Speech-to-Text AI converts spoken language into text, enhancing communication and productivity across various industries.
Powered by Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), it uses sound wave analysis and linguistic models for accurate transcription.
Real-time sub-70ms latency enables fast, accurate transcription, perfect for high-paced environments like customer service and healthcare.
Speech-to-text is widely used in call centers, healthcare, content creation, and more, streamlining operations and improving accessibility.
When choosing a solution, prioritize customization, language support, and enterprise-grade security to meet your business needs.
What Is Speech-to-Text?
Speech-to-text is the process of converting spoken words into written text. It’s commonly known as voice-to-text, and it's primarily delivered as a software-as-a-service (SaaS) offering. Speech-to-text technology is an intersection of linguistics and AI, designed to bridge the gap between spoken communication and written records.
The Evolution of Speech-to-Text Systems
The evolution of speech-to-text systems has been shaped by advancements in AI, deep learning, and data science.
1950s–1960s: Early systems like AUDREY and IBM's Shoebox could recognize a limited set of words and numbers.
1970s: Carnegie Mellon’s HARPY system expanded vocabulary to 1,000 words.
1980s: IBM’s Tangora system used statistical methods to recognize up to 20,000 words, setting the stage for modern dictation systems.
2000s–Present: With the advent of deep learning, speech recognition accuracy improved significantly, enabling systems to capture nuances and adapt to accents and informal expressions. Today, AI-powered virtual assistants integrate speech recognition with natural language processing (NLP), offering more intuitive and accurate solutions.
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let's look at how speech-to-text works in action.
How Does Speech-to-Text Work?
On the surface, human and computer systems appear to share a similar three-part speech recognition process. Here’s how they compare:
Aspect | Human | Computer/Smartphone |
Input | Received via the ears | Received via microphone |
Converted | Into neural signals | Into digital code |
Processed | By cross-referencing with existing knowledge | By cross-referencing with a word-signal library |
At the heart of speech-to-text are advanced Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems, which rely on multiple algorithms and models to deliver fast, reliable results. Let’s walk through how this process unfolds.
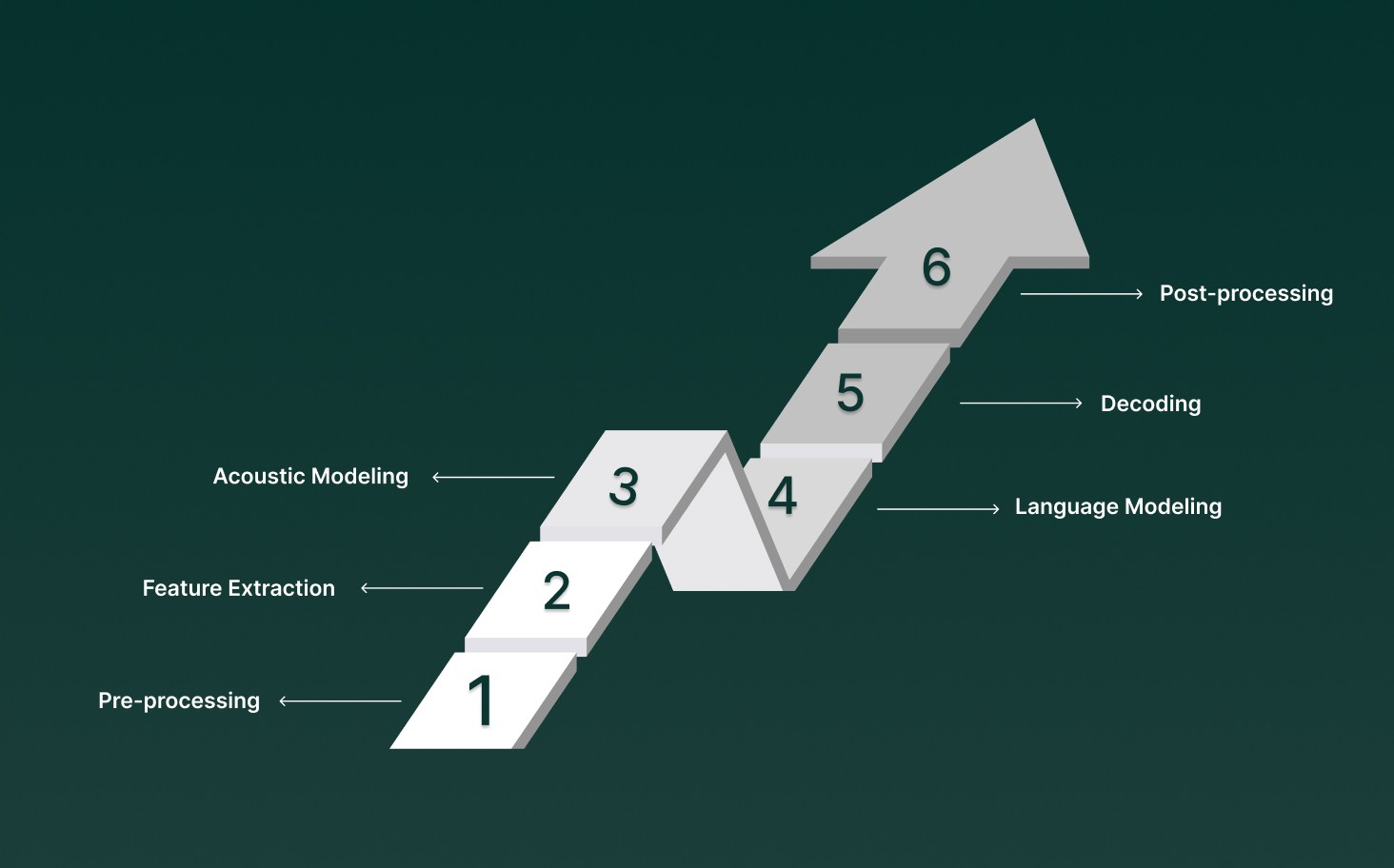
1. Pre-processing
Before any actual transcription begins, the audio input undergoes pre-processing to ensure it's in the best shape for recognition. This involves:
Noise reduction: Filtering out background noises.
Echo cancellation: Reducing any reverberation that may interfere with clarity.
These techniques are crucial for ensuring the audio signal is clean and easily understandable by the system.
2. Feature Extraction
Once the audio is prepped, the next step is feature extraction, where the system breaks down the sound into more useful representations. Key characteristics, such as frequency, amplitude, and duration, are extracted to identify patterns in the speech.
3. Acoustic Modeling
At this stage, the system maps the features extracted from the audio to phonemes, the smallest units of sound that make up words. This requires a statistical model trained on vast amounts of speech data, which helps the system understand how sounds are related to language.
4. Language Modeling
Language modeling is where the system gets “smarter” by considering the context of the speech. Instead of recognizing words in isolation, it predicts which words are most likely to follow others, improving accuracy. This is done through probabilistic models that account for the structure and syntax of the language.
5. Decoding
Once the audio features and language models are aligned, the system uses both to decode the speech. This phase involves:
Searching for the most probable sequence of words that corresponds to the audio input.
Converting the audio features into words or tokens.
This is where the system’s real intelligence shines: combining linguistic knowledge with sound features to produce accurate transcriptions.
6. Post-processing
Even after decoding, errors such as misrecognitions or homophones (words that sound the same but have different meanings) can still occur. To resolve these:
Language constraints and grammar rules are applied.
Contextual analysis helps to refine the output, ensuring the transcription is coherent and free from common mistakes.
Today, major companies like Google and Microsoft offer speech-to-text capabilities through APIs, enabling businesses to integrate transcription into their services.
Also Read: Which AI Tools Offer Multilingual Support for Enterprise Voice Operations?
Understanding the process is important, but it’s also helpful to see where speech-to-text is making an impact.
Key Use Cases for Speech-to-Text Technology
Speech-to-text technology has become an integral tool for various industries, offering practical solutions to everyday challenges. Here's a breakdown of its most significant use cases:
1. Call Center Insight and Agent Assist
Speech-to-text software can automatically transcribe customer conversations, making it easier to track and analyze interactions. It helps route calls by urgency and provides real-time insights into customer sentiment. This technology also helps identify recurring issues and trends in customer satisfaction.
2. Real-Time Transcription and Translation Services
Speech-to-text tools can transcribe online meetings, webinars, and live events in real-time. The transcriptions can be used to generate captions or subtitles for videos, making content more accessible to a global audience.
3. Voice Recognition and Command Execution
Using natural language processing, speech-to-text systems can interpret spoken words to perform tasks such as making phone calls, conducting web searches, or controlling smart home devices. These systems understand commands and execute them seamlessly.
4. Voice Typing and Dictation Apps
For those with physical disabilities, voice-to-text applications offer a valuable way to interact with computers and smartphones without typing. This is particularly beneficial for people with conditions like dyslexia or recent physical injuries.
5. Content Monitoring
Speech-to-text software can also be used to scan transcripts of audio and video content for inappropriate language or harmful material. It acts as an additional layer of monitoring, helping content creators flag problematic material for further review.
From streamlining customer support to improving accessibility and content moderation, it’s clear that this technology is here to stay, shaping a more efficient, responsive future.
See how Smallest.ai’s Pulse delivers real-time, highly accurate speech-to-text solutions, enabling businesses to effortlessly transcribe customer interactions, enhance accessibility, and drive smarter decision-making across industries.
While speech-to-text technology offers significant advantages in various industries, it’s important to recognize the limitations that can impact its effectiveness in certain scenarios
Speech-to-Text: Limitations and Areas for Enhancement
While speech-to-text technology has made significant strides in automating tasks, it still has limitations that prevent it from reaching its full potential. Here are the main challenges:
1. Accuracy Issues
Speech-to-text systems, like most AI-driven technologies, are prone to errors. While transcription accuracy has improved, it’s still not perfect. Human verification is often required to correct mistakes in AI-generated transcripts.
Variation in Performance: Different algorithms perform at varying levels of accuracy. For example, platforms like ContentFries outperform automatic captions found on many social media sites.
Room for Improvement: As technology advances, speech-to-text will likely match or surpass human typists in error rates, but this is still a work in progress.
2. Accent Recognition
One of the biggest challenges is accurately transcribing diverse accents. Many speech-to-text systems are primarily trained on American English, making it difficult for speakers with non-American accents to get accurate transcriptions.
Limited Adaptability: People from regions like Asia, Eastern Europe, and even the UK often face issues with misinterpretation by popular speech-to-text platforms.
Lack of Progress: While there is growing awareness of the need for better accent recognition, many free speech-to-text services still struggle in this area, leaving many users underserved.
3. Vocabulary Limitations
Language advances rapidly, and speech-to-text systems often struggle to keep up. New slang and phrases commonly used on social media may not be recognized by older transcription systems.
Outdated Libraries: Mass-market platforms may fail to recognize trending terms, leaving content creators with issues.
Better for Creators: Content-focused platforms, like ContentFries, often update their libraries to stay current with emerging terms, offering a better experience for those in dynamic industries.
4. Background Noise and Context
Although not always highlighted, background noise and context comprehension are significant barriers as well. As AI continues to improve, these systems will become better at filtering noise and understanding speech in context.
As speech-to-text technology continues to grow, we can expect improvements in accuracy, accent recognition, vocabulary updates, and noise filtering.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of speech-to-text software continue to outweigh its limitations, making it a valuable tool across diverse applications. Here’s a detailed look.
Benefits of Using Speech-to-Text Software

Speech-to-text software enables real-time conversion of spoken language into text, creating vast improvements in speed, accuracy, and workflow.
Saves Time: Automated transcription significantly reduces the time spent on manual note-taking and audio transcription. Businesses can use real-time transcription to convert calls and meetings into actionable text without delay, enabling faster decision-making.
Cost-Efficient: The cost of speech-to-text software is typically far lower than hiring a dedicated team of transcriptionists. Even when subscription fees apply, they are a fraction of the cost of human transcription services, making it an ideal solution for businesses looking to save resources.
Enhanced Content Accessibility: Speech-to-text technology enables real-time subtitling for video and audio content, improving accessibility for hearing-impaired users. It also helps create searchable content archives, which makes large volumes of media more manageable and discoverable.
Improved Customer Experience: By utilizing natural language processing (NLP), speech-to-text software enhances customer interactions, especially in call centers. It can easily integrate with existing systems to streamline customer service, making interactions faster, smoother, and more efficient.
Improved Accuracy & Speed: With advanced machine learning models continually refining their understanding of accents, speech patterns, and context, modern speech-to-text systems offer industry-leading accuracy and can transcribe speech far faster than manual typing.
Speech-to-text technology is a necessity for businesses aiming to stay ahead. By integrating this powerful tool, companies can gain an edge in the competitive business environment.
Also Read: Why Nvidia GPUs Struggle with Real-Time Speech Inference
While there are clear benefits, it’s important to consider a few key factors before choosing the right solution for your needs.
Factors to Consider When Opting for Speech-to-Text Solutions
When choosing a speech-to-text app, several factors should be considered to ensure it meets your needs effectively. With a range of options available, focusing on the right features can help you make the best choice.
Ease of Use: If the app is difficult to navigate or requires a steep learning curve, it could slow down your workflow. Look for apps that are easy to set up and operate, especially for teams without technical expertise.
Price and Subscription Model: It’s essential to assess the pricing and whether the premium features are worth the investment. Free apps can handle basic tasks, but for more advanced features and better performance, consider a paid solution.
Language Support: Choose an app that offers multiple languages and dialects, or even allows customization for specific accents or jargon. This flexibility can improve accuracy and broaden usability.
Accuracy and Performance: The app you choose should reliably convert speech to text without frequent errors. A higher-quality app will handle various speech nuances, such as tone, speed, and background noise, without sacrificing accuracy.
Integration with Other Tools: It’s important that your speech-to-text app integrates smoothly with existing systems, such as CRM platforms, help desks, or customer service tools.
Security and Privacy: Ensure the app complies with industry standards, such as SOC 2 and HIPAA. Features like end-to-end encryption and user access control are also essential for safeguarding sensitive information.
Customization and Flexibility: Look for apps that allow customization, whether it’s adding specific industry terms or adapting to particular speech patterns. This flexibility ensures the app can meet the unique needs of your business or personal requirements.
Customer Support and Updates: Choose a solution that offers easy access to support channels and ensures that the app is regularly updated with new features, improvements, and security patches.
Ready for a speech-to-text solution that offers unmatched security, seamless integration, and full customization? With Pulse STT from Smallest.ai, you get real-time transcription, advanced language support, and the flexibility to tailor it to your unique needs, while ensuring your data remains secure with top-tier compliance standards.
Also Read: Engaging Text-to-Speech Bots for Better Customer Interaction
Why Choose Pulse STT for Your Speech-to-Text Needs?
When it comes to speech-to-text AI, Pulse STT from Smallest.ai delivers unmatched accuracy and performance. Here’s how it meets the key requirements for businesses looking to optimize transcription and communication workflows:
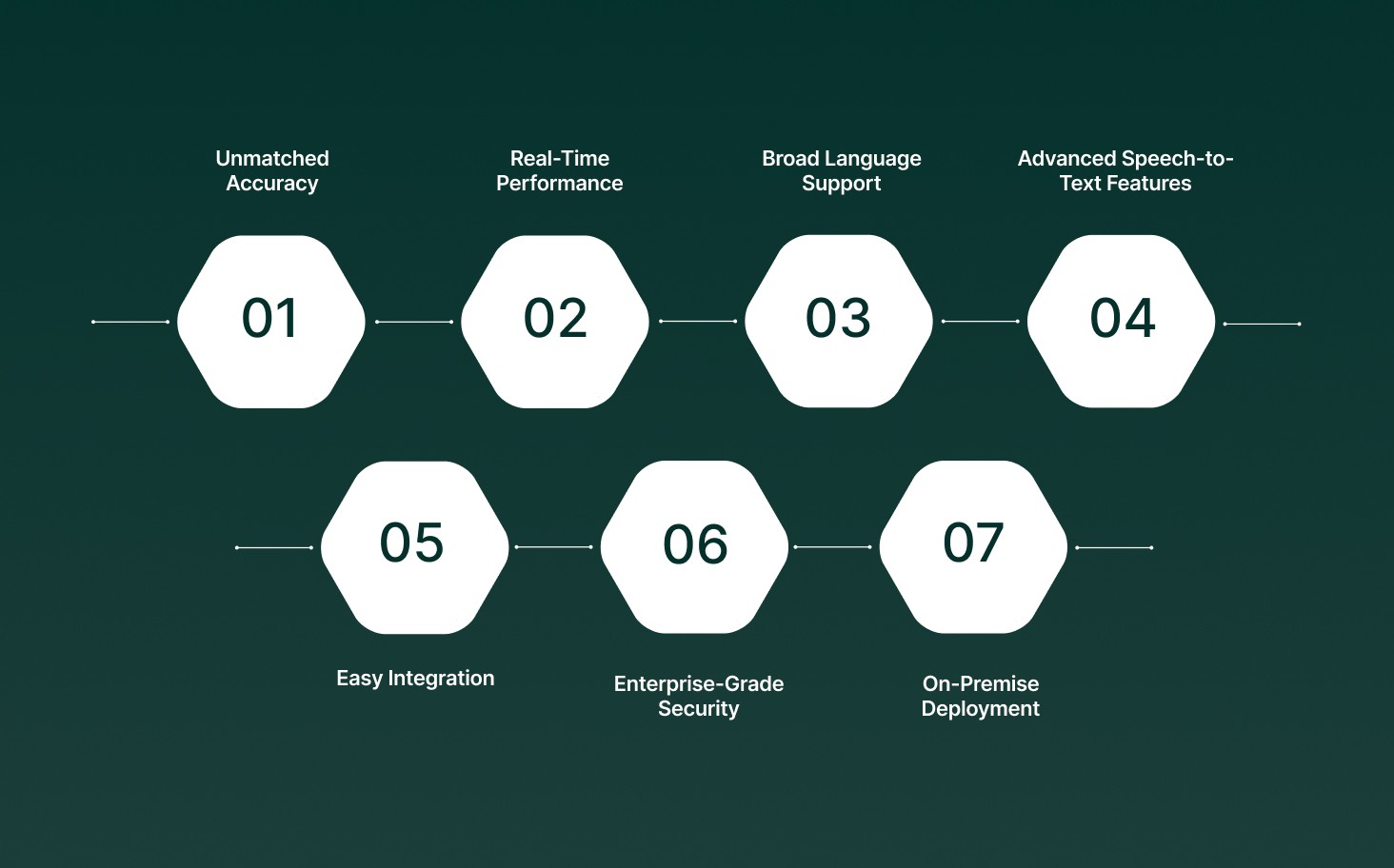
Unmatched Accuracy: Pulse STT achieves the lowest word error rates (WER) across 30+ languages, ensuring highly accurate transcriptions, even in challenging environments.
Real-Time Performance: Enjoy sub-70ms latency for instant transcription, making it ideal for real-time communication in customer service, healthcare, and more.
Broad Language Support: With transcription capabilities in 30+ languages, Pulse STT supports global accents and dialects, making it perfect for businesses with diverse, international teams or clients.
Advanced Speech-to-Text Features: Pulse STT includes emotion recognition, speaker diarization, and automatic language detection with code-switching, ensuring clear, empathetic, and seamless interactions across multi-language environments.
Easy Integration: Pulse STT integrates seamlessly with your existing tools and workflows via Python and Node.js SDKs, providing a simple API to automate and scale operations.
Enterprise-Grade Security: Your data is protected by SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and PCI compliance standards, whether in the cloud or deployed on-premises.
On-Premise Deployment: For ultimate data sovereignty and low latency, deploy Pulse STT directly on your infrastructure, keeping sensitive data fully under your control.
Pulse STT does more than convert speech to text; it delivers fast and secure transcriptions that easily integrate into your operations, helping you stay ahead.
Conclusion
As businesses continue to advance in today’s data-driven world, leveraging Speech-to-Text AI can offer a significant competitive edge. Whether you’re enhancing customer service or integrating real-time transcription into your workflow, the right speech-to-text solution can save valuable time and improve overall operational efficiency.
Pulse STT from Smallest.ai is built to address these challenges head-on. With industry-leading accuracy, it allows you to streamline communication and deliver faster, more accurate services to your clients and customers.
Experience flexibility and security with Pulse STT. Get started today and see how it can transform your business workflows.
Answer to all your questions
Have more questions? Contact our sales team to get the answer you’re looking for

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now


