Build voice agents for logistics to boost efficiency, cut costs, and streamline operations. Enhance customer support and make data-driven decisions today!

Akshat Mandloi
Updated on
January 27, 2026 at 4:57 PM

Logistics bottlenecks are no longer limited to warehouses or delivery routes — they now include something less obvious but just as costly: inefficient communication. Dispatch coordination, driver updates, and customer calls often involve repetitive conversations, long hold times, and delayed actions. As supply chains become more dynamic and real-time coordination becomes critical, AI voice agents are stepping in to fill the gap.
Voice AI is not just a time-saver — it's becoming a cost-saving engine. In fact, over 90% of supply chain leaders expect voice automation to drive day-to-day operational efficiencies, while real-world deployments have already saved millions by reducing fulfillment lag and manual overhead.
This blog explores how to build logistics-ready voice agents — from design to integration — and how they solve communication delays across the supply chain.
TL;DR - Key takeaways
Why Voice AI for Logistics: Manual communication delays hurt dispatch speed and customer experience. AI voice agents automate these repetitive conversations.
How They Work: Real-time voice interfaces use NLP and system integrations (like TMS or WMS) to confirm orders, reroute deliveries, and handle updates.
Build in 5 Steps: Plan use cases, select models, integrate with systems, test in real-world environments, and iterate with real feedback.
Value Delivered: Reduced costs, fewer failed deliveries, faster coordination, and better customer service — at scale.
Why Build an AI Voice Assistant for Logistics and Supply Chain
Communication delays are no longer just a minor issue; they often sit at the center of missed deliveries, failed pickups, and rising costs. As your logistics network expands, manual coordination and fragmented systems quickly become unsustainable.
Here’s why building an AI voice assistant makes business sense for logistics and supply chain operations:
Here are key ways voice AI addresses these issues:
Coordination across teams, drivers, and partners often introduces mistakes and delays. A voice assistant communicates instantly across stakeholders, reducing missteps and improving delivery accuracy.
Language and accent differences slow down exchanges during operations. AI Agents who speak multiple languages smooth out communication and prevent misunderstandings across global teams.
Traditional IVR systems and chatbots require fixed prompts or typed queries, making workflows rigid. Voice agents understand spoken input and respond in context, letting staff interact naturally and work hands-free.
Shrinking time windows pressure operations around the clock. Voice agents handle urgent updates or requests live, cutting the chance that critical data arrives too late.
Manual updates lead to repeated errors and wasted hours. Voice assistants reduce these mistakes by reading real-time info aloud, speeding up fulfillment and reducing rework.
Delays undermine customer trust and drive up support tickets. A fast voice interface delivers timely status updates, improving customer experience and lowering manual inquiry loads.
Costs rise when manual labor fills repetitive tasks. Voice agents take over basic calls and logistics coordination, lowering staff burden and freeing skilled teams for advanced work.
Moving forward, let’s look into how exactly voice AI can make a tangible impact across various areas of logistics and supply chain, showing real-life scenarios where this technology is driving change.
Key Use Cases of Voice AI in Logistics & Supply Chain
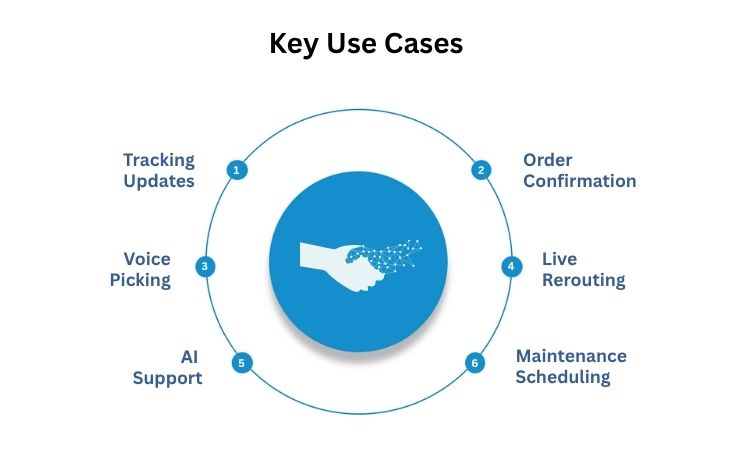
Businesses now face complex logistics involving delivery, inventory, and customer communications. Voice assistants bridge gaps by delivering spoken updates, spoken coordination, and spoken support. The following use cases show how AI Voice Assistants in Logistics and Supply Chain help improve operations.
1. Parcel Tracking and Delivery Updates
Call centers in logistics often face high volumes of status inquiries. AI voice assistants can provide real-time parcel updates based on tracking IDs, without human intervention. This helps reduce the number of inbound support calls to agents while keeping delivery recipients constantly informed. As delivery windows shrink, instant access to tracking details becomes more valuable.
2. Automated order confirmations and rescheduling
Missed confirmations or late reschedules create friction across fulfillment teams. Voice agents can confirm orders and accept reschedule requests through natural conversations over the phone. This reduces the manual effort required by your team while improving communication between operations and customers. The result is fewer missed deliveries and better route efficiency.
3. Warehouse voice-directed picking and stock audits
Within warehouses, voice-guided workflows allow workers to operate hands-free while picking items or conducting audits. Rather than relying on paper instructions or handheld screens, workers receive step-by-step commands via voice assistants. This reduces pick errors, improves speed, and supports compliance with fulfillment timelines during high-volume seasons.
4. Driver coordination and rerouting based on live events
Traffic changes, weather issues, or cancelations require real-time updates to drivers. A voice assistant can notify drivers through short calls, relay instructions, or collect confirmations. This improves route flexibility and reduces delays, especially when managing large fleets across regions. It also eliminates the need for dispatchers to make hundreds of manual calls.
5. AI-powered helplines for B2B or end-customer support
Voice agents can handle common questions, such as invoice queries, delivery timelines, and stock availability. This offloads routine interactions from your service teams and speeds up response times. For B2B partners, quicker access to information means better relationship management without growing support teams.
6. Fleet maintenance reminders and schedule compliance
Missed maintenance creates avoidable delays and safety risks. Voice AI can proactively call drivers or fleet managers to remind them about service schedules. These reminders can also collect confirmations or reschedule appointments, helping you maintain vehicle health without relying on spreadsheets or emails.
With a better understanding of how voice AI fits into daily operations, we can now explore the nuts and bolts of how to actually build one. What does the development process look like, and how can you ensure your voice assistant is up to the task?
Also Read: How AI Voice Agents Are Transforming Communication in Logistics Operations
How to Build a Voice AI Agent in 5 Steps?
Voice AI agents in logistics are more than just speech interfaces; they are designed to manage operational stress, support real-time decisions, and facilitate complex coordination. To make that happen, your development process must align with the pace and priorities of logistics.
Here are five foundational steps that guide the build process for a logistics-ready voice assistant:
Step 1: Plan and understand user requirements
Before writing code or training models, you need a clear understanding of the communication gaps your agent will solve. The planning phase shapes how useful and scalable the solution becomes.
Start by mapping out real-world voice interactions across your workflows:
Identify frequent tasks: Focus on repetitive interactions like order checks, delivery status calls, and rescheduling requests.
Define interaction types: Decide if the agent should handle outbound updates, inbound queries, or hybrid conversations.
Map user journeys: Align dialog flow with tasks performed by warehouse staff, drivers, dispatchers, or B2B clients.
Step 2: Select the right AI and ML models
The model you choose impacts how accurately your assistant can interpret speech and logistics-specific terms. This step determines whether your AI understands real-life operations or struggles with miscommunication.
Once needs are clear, move forward by evaluating model capabilities:
Choose ASR and NLP frameworks: Prioritize engines trained with domain-specific datasets relevant to logistics and fulfillment.
Ensure language flexibility: Support recognition of accents, dialects, or multilingual inputs from regional drivers and vendors.
Plan for domain tuning: Train the model using your route codes, customer names, warehouse zones, and item IDs.
Step 3: Build speech recognition and NLP capabilities
With models selected, you’ll need to construct a system that connects voice processing with your logistics tools. Each part of the assistant must be configured to understand context and respond quickly.
This step includes key integration and design tasks:
Integrate APIs and SDKs: Connect the voice engine to your CRM, ERP, WMS, or dispatch tools.
Design dialog flows: Create structured, task-oriented conversations that avoid unnecessary prompts or ambiguity.
Implement voice UX: Build a user experience around short prompts, fast confirmations, and low-friction input.
Step 4: Test for accuracy, performance, and reliability
No voice agent should go live without rigorous field testing. It must function in high-noise environments and deliver answers in under a second, even under stress.
To validate your build, focus on these performance areas:
Simulate real-world conditions: Test in trucks, warehouses, and low-connectivity zones to catch edge cases early.
Track latency and intent detection: Ensure the agent responds instantly and accurately identifies what the user means.
Evaluate fallback flows: Add graceful exits when audio fails or commands are incomplete, without disrupting workflows.
Step 5: Keep learning and improving
Voice assistants must evolve as your business grows. Continuous feedback helps the system learn, adapt, and cover more ground.
Make your AI smarter over time through these mechanisms:
Collect performance metrics: Use conversation data to refine accuracy, response timing, and user satisfaction.
Update knowledge regularly: Refresh datasets when SKUs change, warehouse layouts shift, or customer policies evolve.
Expand functionality: Start with tracking or dispatch and scale to include inventory queries, invoice status, or onboarding.
If you're serious about building a logistics-ready voice AI, Smallest.ai gives you the speed and infrastructure to do it right. With Waves offering sub‑100 ms text-to-speech and Atoms enabling real-time voice automation, your agent can keep up with warehouse floors and dispatch centers. Their APIs and Python SDKs connect easily to your CRM, WMS, or ERP stack, and everything runs on SOC 2 Type II and PCI-compliant systems, so scale isn’t a risk; it’s a feature.
This structured process gives you a scalable voice AI foundation, designed to fit logistics demands, reduce human bottlenecks, and streamline communication. Before diving into full deployment, there are critical aspects to consider that will ensure a smooth integration into your existing systems.
Key Considerations Before Full Integration
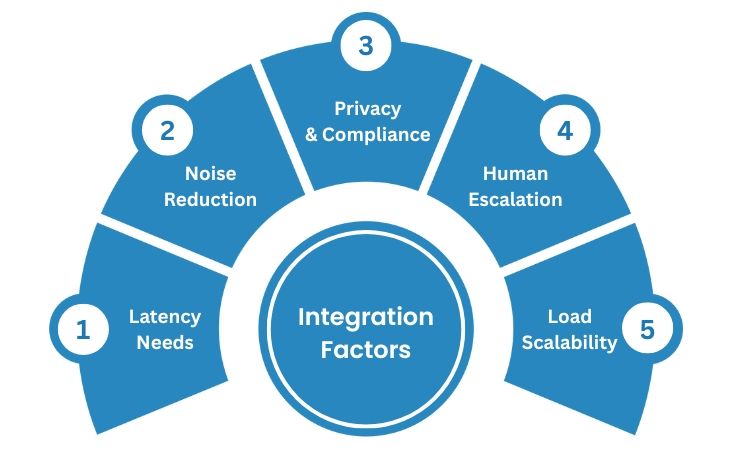
A voice AI agent may pass initial tests, but full integration into logistics operations introduces new operational and technical risks. Ensuring the system meets real-world demands requires evaluating infrastructure, reliability, and compliance before deployment.
Here are the core factors that must be addressed before rolling out voice AI across your logistics stack:
Latency Requirements: Delay in voice response disrupts coordination between drivers, dispatchers, or warehouse staff during time-sensitive operations. Systems must consistently respond within 100 milliseconds to support live rerouting, vehicle coordination, and urgent order updates.
Voice Clarity in Noisy Environments: Warehouses and transit hubs generate constant noise, from forklifts to PA systems. The voice AI engine must isolate speech accurately in environments with ambient sound and motion, or it risks constant errors in intent recognition.
Privacy and Compliance: Sensitive shipment data, customer details, and internal identifiers often surface in voice interactions. All data captured must comply with applicable regulations on personal data (e.g., CCPA, PCI-DSS), especially when stored, logged, or used for training.
Failover to Human Agents: Automated voice shouldn’t become a bottleneck when interactions exceed its capability. A clear handover protocol should be built in, with escalation to human support based on intent confidence, number of failed attempts, or critical query categories.
Scalability Under Load: Peak season or disruptions can double or triple inbound voice requests. Your backend infrastructure must support volume surges without degrading latency or misrouting calls, and scale dynamically during flash demand scenarios like Black Friday or port delays.
Addressing these five areas early gives your logistics voice agent a stable foundation. It ensures performance doesn't collapse under pressure and protects your data, reputation, and operational flow. Now, let’s explore how to measure ROI and make sure your investment is delivering the results you're aiming for.
Also read: Building Efficient AI Voice Bots with Smallest AI
Measuring ROI: How to Know Your Voice Agent Is Delivering
You’ve deployed a voice AI assistant — now it’s time to prove it’s not just “cool tech” but a real operational asset. Measuring ROI should be ongoing, not a post-launch checkbox.
Here’s how to know if your voice assistant is driving value:
1. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
First-Call Resolution (FCR):
Tracks how often inquiries — like delivery updates or driver coordination — are resolved without escalation. Higher FCR = better automation coverage.
Call Handling Time (CHT):
Measure how quickly your agent completes tasks. A drop in average handling time signals higher efficiency across high-volume workflows.
Escalation Rate:
How often does the voice agent hand off to a human? A decreasing trend shows it’s gaining trust and handling complexity better over time.
SLA Adherence:
Track whether shipments, reroutes, or pickups hit their service windows more consistently post-deployment.
2. Voice System Health Metrics
Uptime & System Availability:
Logistics never sleeps — your voice assistant shouldn’t either. Downtime during peak hours (e.g., dispatch windows) creates ripple effects.
Average Response Latency:
Voice agents must respond instantly — especially during dispatch updates or live delivery coordination. Aim for sub-100ms to match real-time needs.
Intent Recognition Accuracy:
Misunderstood commands = operational disruption. Track how well the agent recognizes user intent in noisy, multi-accent environments.
Error Rates (ASR + API Handoffs):
Monitor recognition errors and failed integrations. Frequent dropouts in these systems can indicate model drift or poor data connections.
3. Performance Benchmarking
Use side-by-side comparisons to measure impact:
Metric | Before AI | After AI |
|---|---|---|
Avg. Call Handling Time | 4.5 mins | 1.8 mins |
First-Call Resolution | 62% | 89% |
Agent Handoff Rate | 45% | 18% |
Cost per Routine Inquiry | ₹23.5 | ₹4.7 |
Review these metrics weekly or monthly through your dashboard (like the one offered by Smallest.ai’s Atoms platform) to stay aligned with your goals — whether that’s fulfillment speed, SLA compliance, or team productivity.
Pro Tip: Pair performance reviews with actual business metrics (e.g., delivery speed, warehouse throughput) to surface hidden gains driven by your voice agent.
Why Smallest.ai Is Purpose-Built for Voice in Logistics
Logistics operations don’t run on scripts or predictable workflows — they run on fast-paced, high-stakes decisions where every delay costs money. That’s why Smallest.ai doesn’t offer generic voice bots or retrofitted assistants. It delivers a voice platform engineered specifically for logistics use cases.
Here’s how Smallest.ai stands out:
Sub-100ms Latency for Real-Time Workflows
In logistics, even a half-second delay can disrupt coordination between dispatchers, drivers, and warehouses. Smallest.ai’s Waves engine generates speech responses in under 100 milliseconds - fast enough for dynamic tasks like rerouting, delivery confirmation, or urgent alerts on the move.Context-Aware Agents Trained on Your Data
Forget voice agents that fumble over product codes or location IDs. Smallest’s Atoms platform lets you train agents on your internal logistics vocabulary — from PO numbers and SKU references to route designations and regional warehouse codes — so every response reflects operational accuracy.Built for Scale and Multilingual Operations
Need to handle 5,000 concurrent calls during a shipping disruption or holiday spike? Smallest.ai automatically scales during load surges. With voice recognition tuned for 100+ accents and over 30 languages, you can serve global partners and regionally dispersed teams without compromising clarity.Enterprise-Grade Security and Compliance
Whether you’re dealing with invoice data, shipment details, or fleet location updates, Smallest.ai ensures all voice interactions are encrypted and compliant with SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. You don’t just scale — you scale securely.Seamless Integration, No Rebuilds Required
Smallest.ai integrates natively with CRMs, WMSs, TMSs, and other logistics tools via its flexible APIs and Python SDK. You don’t need to overhaul your stack — just layer on real-time voice intelligence where it fits best.
Smallest.ai isn’t another voice tool — it’s a logistics-specific communication layer that understands speed, scale, and systems integration. Whether you’re coordinating across depots or responding to live delivery changes, it’s built to keep your ops moving forward.
Wrapping Up
Bringing voice AI into your logistics and supply chain operations isn’t about keeping up with trends; it’s about solving real problems. From reducing delays in dispatch to streamlining warehouse communication and improving customer interactions, voice agents can eliminate friction across your workflows. The right implementation helps your team move faster, respond smarter, and operate with more consistency during peak or pressure scenarios.
At Smallest.ai, we’ve built voice agents that understand the pace and precision of logistics demands. We don’t offer generic bots; we design AI that speaks your language, adapts to your systems, and works at the speed of your business.
If you’re ready to reduce coordination lag and add a real-time layer to your operations, we’re ready to help. Book a demo and see what real voice AI can do for your supply chain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can AI voice tools really handle logistics communication reliably?
Voice assistants manage high volumes of routine tasks, like order status updates, rescheduling, and driver coordination, with accuracy and speed. They fit naturally into workflows where consistency and scale outweigh judgment-intensive decision making.
2. Is voice AI truly applicable across warehouse and driver workflows?
Yes, voice AI fits naturally into hands-busy, eyes-busy environments like warehouses and in-transit vehicles. It enables real-time status checks, routing assistance, and task updates without needing screens or manual input. This reduces delays and improves operational speed.
3. Will voice assistants replace human roles in the supply chain?
Voice assistants are designed to support, not replace, human workers. They handle repetitive, high-volume communication tasks so your teams can focus on problem-solving and escalation scenarios. Human oversight remains essential for edge cases and judgment-based decisions.
4. Can voice assistants actually reduce manual dispatch work in logistics?
Absolutely, voice agents manage routine dispatch calls, status updates, and rescheduling automatically. This lowers the communication load on your dispatch team, speeds up resolution times, and improves SLA compliance.
5. How do logistics teams differentiate a real voice agent from a scripted workflow?
Voice agents built with conversational AI adapt to natural, unscripted speech and respond contextually. In contrast, scripted bots follow pre-set flows and often fail when users go off-track or ask unexpected questions.

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now