Find the best AI voice agent frameworks for enterprise in 2025. Enhance operations with LangChain’s modularity, Google Vertex’s security, and AutoGen’s multi-agent capabilities. Choose the right solution and transform your business today. Click to explore top options!

Prithvi Bharadwaj
Updated on
December 26, 2025 at 11:27 AM

Enterprise contact centers are evolving beyond legacy IVR menus and scripted chatbots. Customers expect natural, real-time conversations — and businesses need systems that can scale to thousands of simultaneous calls without losing accuracy or compliance. This is where AI voice agent frameworks come in.
These frameworks form the backbone of intelligent voice automation. They determine how agents process speech, manage context, use external tools, and integrate with enterprise systems. Choosing the right framework can be the difference between a responsive, compliant deployment and one that frustrates both customers and operations teams.
In this guide, we examine what makes a framework enterprise-grade, review the seven leading agent frameworks in 2025, and outline how enterprises can evaluate them for call center automation.
Key Takeaways
Frameworks ≠ voice platforms. Use LangChain/LangGraph, AutoGen, Semantic Kernel, CrewAI, OpenAI Agents SDK, Google ADK, LlamaIndex for orchestration—and add a real-time voice stack for calls.
Latency wins calls. Budget end-to-end (telephony → STT → reasoning → TTS). Sub-second round-trip is the bar for natural turn-taking.
Choose by ecosystem. Microsoft shops lean Semantic Kernel; Google Cloud shops lean ADK; multi-cloud teams favor LangChain/LlamaIndex.
Compliance needs architecture. Pair frameworks with on-prem/VPC deployments and data-handling guardrails.
What makes an enterprise-grade voice agent framework?
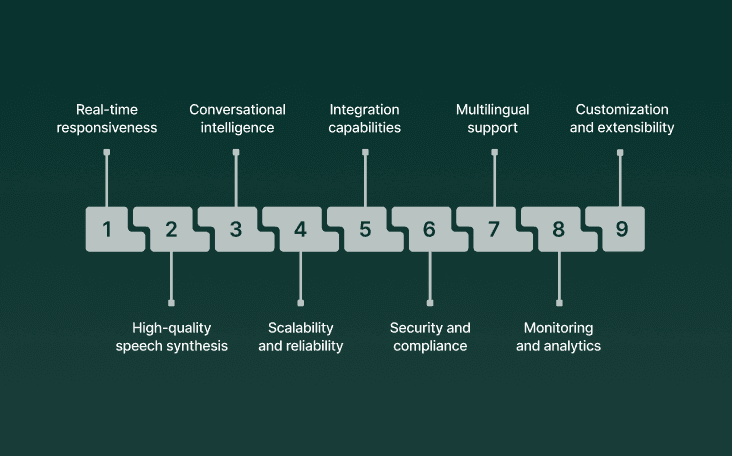
Not every AI voice solution is built for enterprise use. While startups and SMBs may experiment with lightweight tools, large-scale contact centers need frameworks that meet strict performance, compliance, and integration requirements. Here’s what to look for:
1. Real-time responsiveness
Sub-second latency is non-negotiable. Customers won’t tolerate awkward pauses. Frameworks should achieve <100 ms response times.
2. High-quality speech synthesis and recognition
Accuracy across accents, noisy environments, and domain-specific terms.
Expressive voices that sound natural and human-like, avoiding robotic tones.
3. Conversational intelligence
Ability to manage context across long dialogues, interruptions, and back-and-forth exchanges.
Integration with orchestration engines for task completion, not just chit-chat.
4. Scalability and reliability
Capable of handling thousands of concurrent calls with uptime SLAs.
Built-in redundancy, failover, and fallback options.
5. Integration capabilities
Seamless connectivity with CRMs (Salesforce, Zendesk), telephony, databases, and workflow engines.
APIs or SDKs for developers to extend functionality.
6. Security and compliance
SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, PCI readiness.
Options for on-premises or hybrid deployments to satisfy data residency requirements.
Encryption for voice streams and stored transcripts.
7. Multilingual support
Enterprises often serve global customers. A framework should cover at least 10+ languages with accent robustness.
8. Monitoring and analytics
Dashboards for tracking metrics such as containment, average handle time (AHT), and customer satisfaction (CSAT).
Logs and insights to improve both AI performance and business workflows.
9. Customization and extensibility
Ability to fine-tune models, customize voice personas, and adapt flows to brand requirements.
Support for domain-specific terminology (finance, healthcare, logistics).
Leading AI voice agent frameworks in 2025
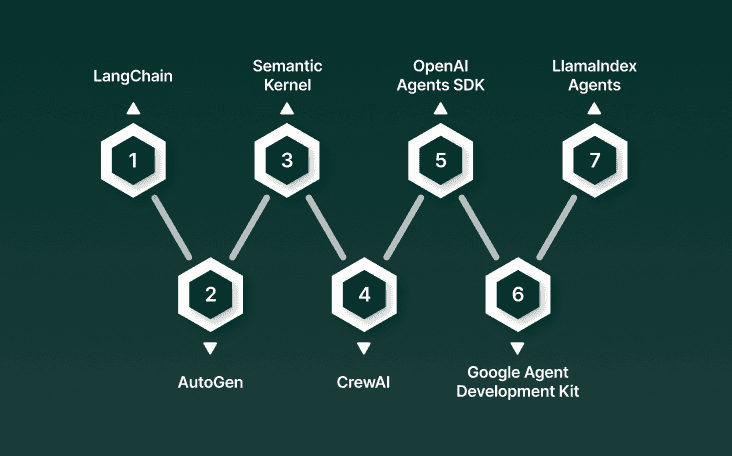
Enterprises evaluating call center automation need to understand the core agent frameworks shaping the market. These frameworks are the backbone for building AI voice agents — providing orchestration, memory, tool usage, and integration capabilities. Below are the seven most relevant frameworks in 2025.
1. LangChain (with LangGraph)
LangChain remains the most widely used framework for orchestrating LLM-powered agents. It lets developers chain prompts, manage context, and connect agents with external tools or APIs. In 2025, the introduction of LangGraph added stateful workflow management, allowing developers to design controlled, branching agent flows.
Strengths: Mature ecosystem, broad integrations (databases, CRMs, APIs), large developer community, deployment tools (LangServe, LangSmith) for production monitoring.
Trade-offs: Not voice-native; requires separate ASR, TTS, and telephony handling. Frequent updates can cause versioning issues.
Best fit: Enterprises with in-house engineering teams that need flexibility to design custom agent logic for call centers.
2. AutoGen (Microsoft Research)
AutoGen is a framework built around multi-agent collaboration. It lets developers define how agents — such as a planner, executor, and reviewer — coordinate to complete complex tasks. For call centers, this can map to workflows where different agents handle transcription, compliance checks, and customer responses.
Strengths: Supports agent-to-agent dialogue, modular workflow decomposition, fast prototyping of multi-role automation.
Trade-offs: Communication overhead can impact latency in real-time use cases; requires careful orchestration design to avoid loops.
Best fit: Enterprises exploring multi-step call workflows where separating roles into distinct agents improves reliability and auditability.
3. Semantic Kernel (Microsoft)
Semantic Kernel is Microsoft’s open-source agent framework designed to connect LLM reasoning with code-based “skills.” It emphasizes structured orchestration through planners and skill libraries, making it a strong option for enterprises already working within Microsoft’s Azure ecosystem.
Strengths: Seamless integration with Azure Cognitive Services (speech recognition, TTS), enterprise-ready security, skill-based orchestration.
Trade-offs: Less flexible for emergent agent behaviors compared to LangChain or AutoGen; not voice-native.
Best fit: Enterprises standardized on Microsoft stack who want a reliable way to embed agent logic in existing applications and workflows.
4. CrewAI
CrewAI is an open-source framework that treats agents as a team of collaborators. Each agent is assigned a specific role — such as researcher, planner, or executor — and they coordinate to achieve a shared outcome. This role-based design helps reduce chaos in multi-agent systems by enforcing clearer boundaries and responsibilities.
Strengths: Role clarity for agents, developer-friendly templates, quick prototyping of collaborative workflows.
Trade-offs: Ecosystem is smaller compared to LangChain; not optimized for low-latency or voice-first use cases; scaling to production requires careful orchestration.
Best fit: Enterprises experimenting with modular agent collaboration — mapping business roles into automated agents.
5. OpenAI Agents SDK (Swarm)
OpenAI’s Agents SDK (sometimes referred to as Swarm in its experimental form) is a lightweight toolkit for defining, coordinating, and deploying agents. It emphasizes simplicity, making it easier to connect LLMs with external tools and APIs while avoiding heavy orchestration overhead.
Strengths: Easy integration with OpenAI APIs, lightweight design, strong support for tool calling and structured outputs.
Trade-offs: Still experimental; tied closely to OpenAI’s ecosystem; requires additional infrastructure for voice pipelines and compliance.
Best fit: Enterprises already invested in OpenAI APIs, looking for a straightforward framework to build controlled, tool-using agents.
6. Google Agent Development Kit (ADK)
The Google Agent Development Kit (ADK), released in 2024, is an open-source framework optimized for Gemini models. It provides structured building blocks for agent orchestration, memory, and planning, enabling developers to design more predictable workflows.
Strengths: Gemini-optimized, open-source, built-in support for planning and multi-agent collaboration.
Trade-offs: Works best with Google Cloud; adoption is still early; not specialized for real-time voice automation.
Best fit: Enterprises committed to Google Cloud or experimenting with multimodal (voice + text + vision) agents.
7. LlamaIndex Agents
LlamaIndex started as a framework for retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and has evolved to support agent workflows. Its agent features allow LLMs to reason across structured and unstructured data, use tools, and interact with enterprise knowledge bases. This makes it especially valuable for data-heavy industries.
Strengths: Strong retrieval-augmented workflows, good for data-grounded conversations, active open-source community.
Trade-offs: Not voice-native; scaling complex agent flows requires engineering effort; smaller enterprise footprint compared to Microsoft or Google.
Best fit: Enterprises with large internal knowledge bases (support manuals, compliance docs, product catalogs) looking to power data-aware voice agents.
Wrapping up the top 7
These seven frameworks represent the state of the art in agent orchestration for enterprises in 2025.
LangChain, AutoGen, and Semantic Kernel are the most enterprise-ready today.
CrewAI, OpenAI’s SDK, and Google ADK are promising newer options with different philosophies (lightweight vs role-based vs multimodal).
LlamaIndex remains the strongest for data-grounded workflows.
For call center automation, none of these frameworks are “plug and play” for voice — enterprises must add speech-to-text, telephony integration, text-to-speech, and compliance layers. That’s where specialized vendors and platforms come in, including solutions like Smallest.ai Voice Agents, which bring the real-time voice stack on top of these frameworks
How to choose the right framework for your enterprise
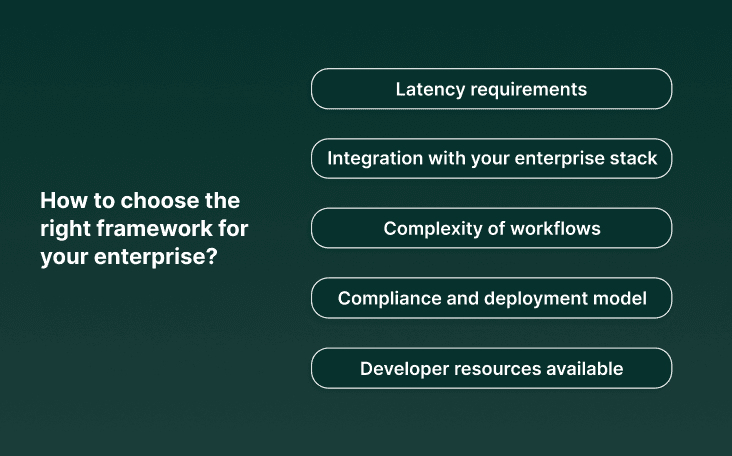
With so many frameworks available, the best choice depends less on “which is most popular” and more on which aligns with your enterprise’s priorities. Here are the key decision factors:
1. Latency requirements
For call center automation, responsiveness is critical. Any framework you choose must be paired with real-time speech-to-text (STT) and text-to-speech (TTS) pipelines capable of sub-second latency. Frameworks like LangChain + LangGraph or AutoGen can orchestrate logic, but you’ll need to layer on a real-time voice stack.
2. Integration with your enterprise stack
Microsoft-heavy organizations: Semantic Kernel is a natural fit, given its tight Azure integration.
Google Cloud adopters: Google ADK works best with Gemini and GCP services.
Multi-cloud or hybrid setups: LangChain and LlamaIndex offer more flexibility.
3. Complexity of workflows
Simple, single-agent tasks: OpenAI’s Agents SDK provides a lightweight entry point.
Multi-step or multi-role workflows: CrewAI and AutoGen are stronger choices for distributed agent responsibilities.
Data-heavy workflows: LlamaIndex excels when voice agents must ground answers in internal documents.
4. Compliance and deployment model
If your enterprise operates in regulated industries (finance, healthcare), compliance posture matters. Frameworks themselves rarely guarantee compliance — they need to be deployed alongside enterprise-grade voice AI infrastructure that supports SOC 2, HIPAA, or PCI. That’s why many enterprises combine frameworks with providers like Smallest.ai On-Prem for data residency and security.
5. Developer resources available
If you have a strong engineering team, open frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, or CrewAI give you flexibility.
If you need faster time-to-market, managed SDKs like OpenAI Agents or more opinionated frameworks like Semantic Kernel may be better.
Implementation best practices and pitfalls
Choosing a framework is only half the battle. Successful call center automation depends on how you implement and operate your AI voice agents. Below are proven practices — and common traps to avoid.
Best practices
1. Budget for end-to-end latency
Measure the full path: telephony → STT → framework logic → TTS → audio playback.
Optimize for streaming pipelines so customers don’t feel delays.
2. Design for barge-in and interruptions
Real customers interrupt agents mid-sentence. Ensure your stack can detect and handle barge-ins gracefully without dropping context.
3. Use domain-specific vocabularies
Customize STT and TTS models for your industry (finance, healthcare, logistics).
Improves accuracy on jargon, acronyms, and product names.
4. Implement guardrails and escalation paths
Define failure modes: low-confidence recognition, out-of-scope requests, or regulatory triggers.
Escalate to a human agent with full transcript and metadata so the customer doesn’t have to repeat themselves.
5. Build compliance in from day one
Redact personally identifiable information (PII) from logs.
Encrypt call data in transit and at rest.
Deploy on-prem or VPC if regulatory requirements demand it. See Smallest.ai On-Premise.
6. Continuously monitor and retrain
Track metrics like containment rate, average handle time (AHT), escalation percentage, and CSAT.
Use weekly transcript reviews to identify common failures and update agent logic.
Pitfalls to avoid
1. Over-focusing on the framework alone
Frameworks provide orchestration, but real-time voice performance depends on your STT/TTS layer. Don’t underestimate this.
2. Ignoring telephony constraints
Dropped calls, jitter, and routing issues often cause more failures than the agent itself. Integration with enterprise telephony must be robust.
3. Skipping pilot phases
Moving straight to full rollout risks brand damage. Start with a limited pilot flow, measure performance, and iterate.
4. Neglecting handover experience
Customers judge automation by how smoothly it escalates to humans. Poor handover creates frustration, even if the AI works 90% of the time.
5. Assuming compliance comes “out of the box”
Frameworks aren’t certified — the way you deploy them matters. Pair them with compliance-ready infrastructure like Smallest.ai Voice Agents.
Also read: Lightning: Fastest Text-to-Speech Model by Smallest.ai
Conclusion
The enterprise contact center is no longer just about handling volume — it’s about delivering fast, reliable, and compliant experiences at scale. Agent frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, Semantic Kernel, CrewAI, OpenAI’s Agents SDK, Google ADK, and LlamaIndex are providing the orchestration backbone for these systems, but none of them solve the voice challenge on their own.
Success in call center automation comes from pairing the right framework with a real-time voice stack that can meet enterprise requirements for latency, compliance, and integration. The frameworks outlined here give enterprises the flexibility to choose based on ecosystem, workflow complexity, and internal resources. The final step is deploying them in a way that aligns with operational demands and regulatory obligations.
Ready to see how these frameworks power live conversations? Explore Smallest.ai Voice Agents or review our Enterprise Voice AI Stack guide for practical deployment insights.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between an AI agent framework and a voice AI platform?
An agent framework (e.g., LangChain, AutoGen) provides orchestration, memory, and tool use for large language models. A voice AI platform adds the real-time voice layer — speech recognition, text-to-speech, telephony integration, and compliance features needed for call centers.
2. Which is the best AI agent framework for enterprises in 2025?
There is no single “best” — it depends on priorities.
LangChain + LangGraph: broad ecosystem and flexibility.
Semantic Kernel: tight Azure integration.
Google ADK: optimized for Gemini and multimodal workflows.
LlamaIndex: strongest for retrieval-augmented, data-grounded conversations.
3. Can these frameworks be deployed on-premises for compliance?
Yes, but the compliance posture comes from deployment architecture, not the framework alone. Enterprises often combine frameworks with on-prem or VPC deployments to meet HIPAA, PCI, or SOC 2 requirements. See Enterprise Voice AI On-Premises Deployment Guide.
4. Which frameworks are best for multi-agent collaboration?
AutoGen: strong in multi-agent task decomposition.
CrewAI: role-based orchestration with collaborative workflows.
These are best for complex enterprise processes where tasks need to be split between specialized agents.
5. Do frameworks alone guarantee real-time responsiveness?
No. Frameworks handle reasoning, but real-time latency depends on the speech stack (STT/TTS), telephony setup, and infrastructure optimization. Enterprises aiming for <100 ms responsiveness need frameworks plus a low-latency voice layer like Smallest.ai Voice Agents.

Automate your Contact Centers with Us
Experience fast latency, strong security, and unlimited speech generation.
Automate Now


